Linux mint 18 cinnamon after installation. Installing the required languages, locales and layouts. Removing unnecessary languages and fonts
Linux Mint
is one of the most popular today operating systems Linux.
Developers Linux Mint They release several distributions with different desktop environments: Cinnamon (own development), MATE, Xfce, KDE And LMDE(Rolling release based on Debian, also of our own design).
Xfce it's fast and easy working environment, low consumption system resources. At the same time, it is visually attractive and user-friendly.

This is the desktop Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce With Welcome screen, which displays various links to help a new user get started with the system.
At the bottom of the monitor, as in most distributions, there is a control panel with applets located on it: menus, application quick launch icons, buttons for open windows and the system tray.
The disadvantage of this environment that new users encounter is the absence of a keyboard layout icon after the first login, because... even after opening the browser, the user is at a loss as to how to switch from English to his own native language, although the system was installed and displayed on it?
1. Keyboard layout and hotkey assignments
To display a keyboard layout icon, you need to add it to the panel. To do this, click right mouse button on any free space of the panel and in the menu that opens, select:

When the window opens Adding new elements, select Keyboard layouts and press the button Add:

Note. All newly added elements are always displayed in the right corner of the panel. To move them on the panel, right mouse click on the element/icon, select Move, move it to the desired location on the panel and left clicking pins it.

To assign keyboard layout hotkeys, right-click on the icon and select from the menu Keyboard settings:

In the window that opens Keyboard, in the tab Layout turn off Use standard system settings and in the parameter - Change layout options activate the key combination you need:

Now that we have completed the missing element on the panel, it’s time to update the system, because... after the first login, this must be done Necessarily.
2. System update.
In the system tray, on the panel you should see an icon in the form of a shield with a Latin letter i - Update Manager:

Click on the icon and a welcome window will open Update Manager With possible options update policies:

Select/activate the update item that is more acceptable for you And OK.
Perform a system update by pressing the button Install updates and wait for the system update to complete.
Once all updates have been completed, the icon has been installed and keyboard shortcuts have been assigned, you can now work in the system Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce, as in any other: surf the endless expanses of the Internet and download the necessary files, watch movies, listen to music, print in Libre Office and use a printer, download pictures from the camera and edit them, view your video from a video camera, communicate with family and friends, in general, everything that can be done in a regular operating system.
Note. Next steps, proposed in the article are not mandatory, they simply introduce the system and its capabilities.
3. Setting up the control panel
Right-click on any free space in the panel and select from the menu that opens - Panel Options:

By default, the control panel is located at the bottom of the monitor, but you can move it to top part. To do this, in the panel settings, uncheck the item Lock panel(top photo), now grab the panel by the left or right edge and drag it up:
The control panel can be positioned not only horizontally, but also on the right or left - vertically, with the same arrangement of applets:

Or choose how Side panel and then the applet Window buttons will display more compactly open windows in the form of icons:

The panel can also be resized:

And also select and activate the options for hiding the panel:

Change appearance panels in a tab Appearance:

Here you can customize the solid color, with a choice of color and transparency of the panel.
Adding applets to a panel
I already described adding a keyboard layout applet at the very beginning of the article. Other applets from the proposed default list are added in the same way. Right click on the panel, select Panel - Add New Items:

Removing applets from the panel
Removing applets from the panel is done as follows:
Right click on the applet and Delete:

4. Desktop customization
Right-click on any free space on your desktop and select from the menu that opens - Desktop customization:

In the window that opens Desktop three tabs: Background, Menu And Badges.

In the tab Background can change background image, click on it from the proposed catalog, or activate the parameter Change background at certain intervals and background pictures desktop will change automatically, after a time set by the user.
Tab Badges is responsible for the appearance of the desktop. In it you can activate the display on the table Home folder, Baskets etc. elements, as well as change their size and font size:

Tab Menu serves to configure the menu displayed on the desktop by right-clicking, or by clicking with the middle button (mouse wheel):


5. System settings
Settings systems you can find in Menu by clicking on the icon All settings:


System settings are divided into categories: Personal, Equipment, System And Other. All of them are already set by default, but you can change them at your discretion.
6. Additional programs to install
The system already has necessary programs, which the user can find in the menu. If you haven't found any special program in the menu, then in distributions Linux you don’t have to look for them on the Internet, first of all open them in system menu Program Manager, most likely you can find the necessary additional software:

As you can see in the picture, all programs are divided into categories, which makes it easier to find the one you need. Click on the selected category and view the list of offered programs, or enter the desired name in the search field, click Enter on the keyboard, select the program, click on it and press the button Install:


7. Change window manager
Window Manager — computer program, which controls the placement and determines the appearance of windows in a graphics window system user interface.
IN Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce By default, several window managers are preinstalled.
Open All Settings - Desktop Settings:

And in the parameter Windows - Window Manager select the one you want to use. The manager will change on the fly:

Suppose a window manager has been selected Compiz. It already has some plugins for managing windows and desktop (Desktop Cube) activated:

Change settings Compiz can be pressed on the button Set up Compiz:

8. Installation additional programs on the desktop
Let's add some more goodies or frills to the desktop.
The bottom image shows two widgets: Conky and weather widget GisWeather.

And although the additions to both panels have their own weather elements, I think the widget is the most colorful and accurate for displaying the weather in your area GisWeather.
Installing the widget GisWeather
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gis-weather
Once the installation is complete, you will find GisWeather in programs Tools or search in the menu.
How to customize the widget and display your area, see.
Installation Manager Conky
Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), copy and run this sequence of commands:
sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install conky-manager
After installation you will find Conky Manager in programs Tools or search in the menu.
How to create your own widget Conky, look .
9. Install Skype
Skype — free application, providing text, voice communication and video communication via the Internet between computers (IP-telephony) and mobile devices, optionally using peer-to-peer network technologies, as well as paid services for calls to mobile and landlines.
Program Skype is very popular among Internet users.

Installation Skype
Install Skype
sudo apt install skype
In system 64-bi T, Skype uses a theme Clearlooks instead of the default theme, other themes are also not displayed correctly.
This happens because Skype represents 32-bit application with theme GTK2, where is the engine Murrine in most cases it is not installed.
If you have installed 64-bit system, then fix the theme Skype you can by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt install gtk2-engines-murrine:i386 gtk2-engines-pixbuf:i386
Note. If after installation Skype You don't have a tray icon, just install one plugin. To do this, open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), and run the following command:
sudo apt-get install sni-qt:i386
And restart Skype.
10. Install Systemback - restore the system to a previous state
Systemback Very useful application, which allows you to create backups and restore points of your system.

Peculiarities Systemback
System backup
System Restore
System installation
Creation of Live CD
System repair
System update
Installation Systemback
Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), copy and run the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nemh/systemback
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install systemback
Instructions for use Systemback look .
Conclusion
These are the recommendations that I would like to offer at your discretion after installation Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce.
System Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce After installation and all the settings described above, it works stably, smoothly and looks very beautiful.
Have you ever wanted something better than what's running on your computer now? Whether you use Windows, Mac or Linux, you can see that there are other good systems out there.
What is Linux today?
Linux Mint is one of the most popular and fastest growing operating systems. Today it is a full-fledged replacement for Windows. The advantages of this “shell” are obvious: it is faster, better, easier to use, while its functionality is expanded and protected. In addition, the OS is completely free to use and distribute.
Moreover, Linux Mint is unique in its appearance, easy theme management, large storage facilities software and functionality out of the box.
The OS has four versions or variants:
- Linux Mint Cinnamon is own environment Linux, with Gnome desktop. This version is elegant and functional.
- Mate is another flavor of Gnome used as a classic OS.
- XFCE is a minimalist and elegant desktop environment. It is suitable for computers with low resources.
- KDE is one of the most complete desktop environments that has many functionality and good appearance. It's good for modern computers with the latest equipment.

System requirements for Linux installations Mint:
- 512 MB RAM (1 GB recommended for easy use).
- 9 GB disk space(20 GB recommended).
- Resolution 1024 × 768 (with more low resolutions press ALT to drag windows with the mouse if they don't fit on the screen).
Wherein:
- 64-bit ISO can be booted from using BIOS or UEFI.
- 32-bit ISO - only with BIOS.
- 64-bit ISO is recommended for all modern computers (almost all devices released in the last 10 years have 64-bit processors).
How to make a boot file?
Go to the Linux Mint download site and choose the best option for you. You can choose a download mirror or download a torrent. Depending on the speed of your connection, it may take some time for the download to complete.
To copy an ISO file to a DVD, you will need an image burning program. One of the most popular free options is ImgBurn, although there are many other popular options (Nero, etc.).
Burn a bootable disc. You can also burn the image to a USB drive if you want to install Linux Mint from a flash drive. To do this, you will need to download the Linux application from the official website Live USB Creator.

Use the downloaded software to create installation media. Select the downloaded ISO as the source file. Click the "Record" button to begin the creation process. This may take a few minutes.
Set your computer to boot from a DVD drive or USB. To run Linux Mint, you will need to start booting it from the created media instead hard drive. You can use for this BIOS menu your computer. Make the priority settings so that Linux Mint is installed from a disk or flash drive immediately.
Once your device boots from the media you created, you'll see a short list of options. Select "Launch Linux Mint" to boot the operating system.
This does not install a "shell". Booting the operating system from a DVD or flash drive allows you to test Linux and see its functionality before installing it. You will not be able to change any settings or delete or create files in preview. When running from disk, the shell will run slower than if it were installed.
Once you are familiar with the OS desktop, you can start installing Linux Mint from a flash drive or DVD by double-clicking the “Install Linux Mint” icon located on the desktop. This will launch the installer. Select your language and click Continue.
To use the bundled bootloader, you need to have at least 3.5 GB free space on your hard drive, and active connection to the Internet. If you are installing Linux on a laptop, make sure it is connected to a power source during installation.
The next menu will allow you to select how much hard drive space you would like to allocate to your Linux operating system. There are two main options:

- Clean the disk and install Linux Mint. This option will erase all data on the selected drive and install a new OS on it. Any existing operating systems or data will be destroyed. Use this option if you want Linux to be the only “shell” on your computer.
- Install without deleting data. This option will allow you to use the free space on your hard drive to create a separate partition so that Linux Mint can be installed next to Windows or another OS. This option also allows you to select the partition size.
From the drop-down menu, select which drive you want to install the new “shell” on. If you choose the second option, you will be able to use the slider to set the partition size.
A Linux Mint installation requires at least 6GB for its partitions, and swap partitions should be 1.5 times the size of the RAM you have installed.
How does the installation process work?
Once the installation begins, you will be asked to select your time zone and keyboard layout. You can use the "Arrange Keyboard" button if you are unsure of the default settings.
After selecting your input settings, you will be prompted to enter your name and create a user profile. You can change your username as you wish. The machine name is the name that your computer will display to other devices on the network.
You will also need to create a password. This username and password combination will be your administrator account and must subsequently be entered whenever changes are made to the system. Once the installation of Linux Mint is complete, you will be able to create more user profiles.
Wait for the process to complete. After entering your information, Linux Mint 18 will begin copying files. You can monitor the download progress by looking at the bar at the bottom of the window. Once the files have been copied, the installation will begin and your hardware will be configured.
This process may take some time, especially on older machines. From this moment on, everything happens automatically, so you don’t have to monitor the process.
The bootloader will use additional files during the installation process, so you will need a valid network connection.
Ending the process
Once the installation of Linux Mint is complete, you will be prompted to restart your computer. Click the Restart Now button to boot into the newly installed operating system.

Once the above process is complete, launch Linux Mint Cinnamon and log into your account to go to the desktop. View the welcome screen. It contains links to guides and tips, so take a moment to browse through the resources available. This window will appear every time you start the OS unless you uncheck the box in the bottom right corner.
Customize your desktop
By default, Linux Mint (including the Russian version) will boot with a link to the contents of your computer and your home directory on your desktop. You can add a trash icon to make it more like Mac computer or Windows. To do this, click the "Menu" button in the lower left corner and select " System Settings" From the left side. Click "Desktop" under Settings and check the icons you want to display.
Software
Linux comes with several basic programs such as Firefox, LibreOffice, GIMP Image Editor and VLC Player. You can also install many other applications, most of them are free. To do this, click the "Menu" button, hover your mouse over "Administration" and select "Program Manager". You will be prompted to enter your administrator password.
Programs are sorted by category, but you can also search for specific services. Keep in mind that most Windows and Mac programs are not available for Linux Mint 18, so you will need to find alternatives that perform the same functions.

Installing Wine and/or VirtualBox Wine will allow you to simulate Windows and, accordingly, install or run programs for this OS. However, sometimes this can be quite difficult - some applications will not be fully accessible.
To avoid this, you can install PlayOnLinux. This is a program that makes it easy Windows installation Software (for example, MS Office 2007, games) with boot disk. The second option for running non-Linux software is installing VirtualBox, which creates a virtual partition for running the OS. Basically, you can install and run Windows (or anything else) inside Linux, just like in another window. Then you can install your software on it. You also don't risk breaking Linux Mint.
Install Compiz Fusion
Setting up Linux Mint after installation also includes loading and displaying some of the functionality required for operation and comfortable use OS. Open Synaptic Package Manager, type "simple-ccsm" (without quotes), right-click and check the boxes to install. These include ccsm, as well as compiz, compiz-plugins, compiz-core, compiz-gnome and compiz-fusion-plugins-extra. Make sure they are all checked (use the search box at the top) and then click Apply.
Set up Compiz
Compiz is a window manager that takes full advantage of your graphics card and adds many effects (like rotating your desktop in 3D). Right-click on your desktop and click "change background" to open the Appearance settings. Go to "Visual Effects" and select "custom". Now click on the settings button to open the Simple CompizConfig Settings Manager and go to the Desktop tab.

Select "Desktop Cube" under Appearance. Use 3-5 columns and one table for the desktop. Go to the Effects tab. Select "Shift Switcher (Cover)" as Alt+Tab window switcher.
Find Warp: Cylinder, change the opacity to about 70 and check all the EXCEPT Blur boxes if you don't have a graphics card that can handle it. If your graphics are relatively old/integrated, don't touch this option.
Do instead simple settings. Hold Ctrl + Alt and click and drag the mouse to display the menu. Open CompizConfig Settings Manager. On the main screen, deselect "Denial" and check "Show Mouse". Click "Rotate Cube" and change the scale to 0.4. Go back to the Effects section ( left menu), check "Bicubic Filter" and "Trail Focus". Try using the Paint Fire and Water effects (just enable them and use the shortcuts from the settings page). Now go to "Cube Reflection and Deformation" (check it if it's not already checked), expand Appearance and click on the top image file. Click "Edit" and replace everything with "`" (without quotes). Same for the bottom image. Go through the top and bottom colors of the cube and change the opacity to 0 for both. Now go back to the main screen and check “Window Previews”. Feel free to try other things too. Everyone has different requirements and different tastes.
Install Emerald/Compiz Window Decorator
Go to Package Manager from the main menu. Enter Emerald in the search box above. Right click on it and mark it to install, then apply. Once it's installed, press Alt + F2 (launch a dialog) and type "emerald -replace" (without quotes). You should notice the change immediately. To ensure that the functionality is loaded every time the system boots, add it to the list in “Startup Applications.” Use the same command.
Set up Emerald/Comfiz
When the installation of Linux Mint is fully completed, the instructions for adapting it to familiar operating systems are especially relevant. You can make the borders of your window exactly the way you want, whether it's like Mac Snow Leopard or Windows 7. For this you need Emerald Theme Manager. If it's not already installed, go back to Synaptic (package manager) and install "emerald/comfiz-theme-manager". Then open it and explore. There are literally thousands of themes and settings to choose from. To use them, just go to gnome-look.org -> beryl and download what you would like to download. Then add them via Theme Manager.
Install Synapse to run programs
Just add ppa: synapse-core/ppa to your software sources, update and search for "Synapse" in the Ubuntu Software Center. Open it from the main menu. You can activate it by pressing Ctrl + Space. Type a program to search for and press Enter.
Install the dock
The Dock is a launcher for applications and windows. You have a lot different options for this, including Docky, Cairo-Dock, ADeskBar and AWN. To install any of them, just copy from the official website and paste the commands into Terminal. Go back to synaptic and download additional gstreamer plugins, ms core fonts and Flash.
Today we will look at the operating system distribution Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon, we will download this version, install it on your computer, talk about innovations, and I will also show you the process of updating to this version.
Review of the Linux Mint 18.3 distribution
First, let's remember what Linux Mint is.
Linux Mint is a distribution of the Linux operating system, it is free and is intended for use on home computer. Linux Mint is available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions, supports the Russian language, it is functional, stable and undemanding of resources. Therefore, if you want to use Linux as an operating system on your home computer, then I personally recommend installing the Linux Mint distribution.
Linux Mint can be installed with such graphical shells as: Cinnamon, Mate, KDE and Xfce. As the title of the material suggests, today we will be looking at the version with the Cinnamon desktop environment.
The official website of the distribution is www.linuxmint.com
What's new in Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon?
Codename for Linux Mint 18.3 version " Sylvia", be supported this version will be available until 2021, like the entire line of 18.X versions, it is based on the Ubuntu 16.04 package base.
Major Components and Changes :
- Linux kernel 4.10;
- Cinnamon version 3.6;
- Browser Mozilla FireFox 57.0;
- Mail Mozilla client Thunderbird 52.4;
- Office suite LibreOffice 5.1.6.2;
- Updated program manager ( Software Manager) – probably the main innovation of the current version is the redesigned program manager. It has been redesigned almost completely, including GUI user. Now, by the way, you don’t need to enter a password in order to simply launch the manager for viewing available applications, the password is only required to install these applications. I hope this version will be as convenient as the previous one, which I personally really liked. Currently the program manager looks like this;
- Available popular apps– now programs such as Skype, WhatsApp Steam or Minecraft can be easily installed from the program manager using standard tools;
- Flatpak support – the distribution now supports Flatpak technology. Flatpack is a technology that allows applications to run in an isolated container, making it unimportant which Linux distribution you use. In other words, you may be installing an application that is not compatible with the Linux Mint distribution. The program manager even has a separate category that houses applications developed using Flatpak;
- GNOME Online Accounts Support – Cinnamon now supports GNOME Online Accounts, allowing you to browse Google Drive and OwnCloud in the Nemo file manager;
- Tools Reserve copy: Personal Files and System Snapshots. Tool " Backup" has been completely rewritten and now works in user mode ( those. no need to enter a password), this tool designed to create a backup copy of your home directory. It is also now possible to take system snapshots thanks to the Timeshift functionality, which is designed to take snapshots of the operating system similar to System Restore in Windows;
- System reports - added in this version new tool « System reports", which is designed to generate reports when software failures occur, such reports are called " Crash Reports", as well as for displaying system information, reports " Information Reports»;
- Window Progress ( Window progress) - LibXapp now allows applications to pass their progress to the window manager, in other words, the progress is shown in the panel's window list. This feature is supported the following applications: file manager Nemo ( file operations), backup tool, Timeshift, software manager, driver manager and some other applications that use dialog boxes Synaptic;
- Improvements to XApps applications – e.g. text editor Xed now has a minimap, Xreader detects DPI, Xplayer has improved full-screen window;
- Improved login window - added additional settings, for example, it became possible to hide the list of users and enter user names manually, and various elements on the panel can be disabled and now, by the way, they show tooltips;
- Linux Mint now has improved support for spell checking and synonyms in English, German, Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese and Russian;
- Redshift is now installed by default. This software adapts color temperature screen depending on the time of day, in other words, the screen will be warmer at night, thereby reducing the impact on your eyes.


Backup

Timeshift


![]()

Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon System Requirements
- 1 gigabyte random access memory (recommend more);
- 15 gigabytes of free disk space ( recommend 20 gigabytes);
- Supports screen resolution 1024x768.
The version with Cinnamon is one of the most undemanding in terms of resources and it works really fast.
Where to download Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon?
Download current version operating system Linux Mint 18.3 can be found on the download page of the official website - here it is.
After going to the page, you need to select your desktop environment and system architecture ( 32-bit or 64-bit). Click on the desired link.

Then you need to choose a download method, for example via torrent or from any available mirror, for Russia you can choose Yandex Team, here is a direct link to download Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon 64-bit from this mirror.

As a result, I downloaded the 64-bit version, namely the file ( iso image) linuxmint-18.3-cinnamon-64bit.iso approximately 1.76 gigabytes in size.
Installing Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon on your computer
The Linux Mint installation process is simple, and we have covered it many times already, but for those who will be installing Linux Mint on a computer for the first time, I will describe this process step by step and with pictures.
Step 1
We burn the image that we downloaded to disk and boot from it. After loading, the disk menu will open, select “ Start Linux Mint».

Step 2
Loading Live version, on the desktop, click on the shortcut “ Install Linux Mint", the installation program will eventually start on HDD computer.

Step 3
First, select the language, click " Continue».

Step 4

Step 5
Now we select the disk partition type, I have a test installation, so I select the first item “ Erase disk and install Linux Mint" To manually partition the disk, select " Another variant" We discussed manual partitioning in detail in the material “Partitioning a hard drive in Linux Ubuntu during installation.” In my case, click " Install now».

Confirm the changes by clicking “ Continue».

Step 6
Specify your location and click " Continue».

Step 7
Select the keyboard layout and press the “ Continue».

Step 8
All that remains is to create an account; to do this, enter your name, computer name, username and password with confirmation, click “ Continue».

The installation has started.

The installation is complete when the following message appears, click " Reboot»
Upgrading Linux Mint to Linux Mint 18.3
It is not necessary to install Linux Mint from scratch, if you already have the previous release of Linux Mint 18.2 installed, you just need to update installed system for example using " Update Manager" To do this, open “ Menu ->Administration -> Update Manager».

If there is no update " mint-upgrade-info", then first press the button " Check for updates", and then " Install updates I".

Enter the administrator password, since installing updates requires certain privileges, click " Authenticate».

After you have installed this update, in your menu “ Edit» update manager the item « Update to Linux Mint 18.3 Sylvia", to update the entire distribution we need to click on this item.

As a result, the update program will start. In the first window, click " Next».

Then we are asked to read the release notes ( for this, if you want, you can click on the appropriate link), click " Next».

Before updating, we are asked to find out the new features of this version ( if you want to see them, click on the appropriate link), click " Next».

Next we are warned that there is a risk of harming the system, since after any update some problems may arise, but in standard cases everything goes well, we check the box, thereby confirming our intentions to update the system, and click “ Apply».

To update the system you need to enter your password, click " OK».


The system update will be completed when the following window appears, click “ Close"and reboot the computer.

Screenshots of Linux Mint 18.3 Cinnamon
Desktop

File manager

System parameters

That's all, good luck!
Linux Mint is one of the most popular operating systems today Linux.
Developers Linux Mint They release several distributions with different desktop environments: Cinnamon(own development), MATE, Xfce, KDE And LMDE(Rolling release based on Debian, also of our own design).
Xfce It is a fast and easy working environment, with low consumption of system resources. At the same time, it is visually attractive and user-friendly.

This is the desktop Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce With Welcome screen, which displays various links to help a new user get started with the system.
At the bottom of the monitor, as in most distributions, there is a control panel with applets located on it: menus, icons quick launch applications, open window buttons and system tray.
The disadvantage of this environment that new users encounter is the absence of a keyboard layout icon after the first login, because... Even after opening the browser, the user is at a loss as to how to switch from English to his native language, although the system was installed and is displayed in it?
1. Keyboard layout and hotkey assignments
To display a keyboard layout icon, you need to add it to the panel. To do this, click right mouse button on any free space of the panel and in the menu that opens, select:

When the window opens Adding new elements, select Keyboard layouts and press the button Add:

Note. All newly added elements are always displayed in the right corner of the panel. To move them on the panel, right mouse click on the element/icon, select Move, move it to the desired location on the panel and left clicking pins it.

To assign keyboard layout hotkeys, right-click on the icon and select from the menu Keyboard settings:

In the window that opens Keyboard, in the tab Layout turn off Use standard system settings and in the parameter - Change layout options activate the key combination you need:

Now that we have completed the missing element on the panel, it’s time to update the system, because... after the first login, this must be done Necessarily.
2. System update.
In the system tray, on the panel you should see an icon in the form of a shield with a Latin letter i - Update Manager:

Click on the icon and a welcome window will open Update Manager with possible update policy options:

Select/activate the update item that is more acceptable for you And OK.
Perform a system update by pressing the button Install updates and wait for the system update to complete.
Once all updates have been completed, the icon has been installed and keyboard shortcuts have been assigned, you can now work in the system Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce, as in any other: surf the endless expanses of the Internet and download the necessary files, watch movies, listen to music, print in Libre Office and use a printer, download pictures from the camera and edit them, view your video from a video camera, communicate with family and friends, in general, everything that can be done in a regular operating system.
Note. The further steps proposed in the article are not mandatory; they simply introduce you to the system and its capabilities.
3. Setting up the control panel
Right-click on any free space in the panel and select from the menu that opens - Panel Options:

By default, the control panel is located at the bottom of the monitor, but it can be moved to the top. To do this, in the panel settings, uncheck the item Lock panel(top photo), now grab the panel by the left or right edge and drag it up:
The control panel can be positioned not only horizontally, but also on the right or left - vertically, with the same arrangement of applets:

Or choose how Side panel and then the applet Window buttons will more compactly display open windows as icons:

The panel can also be resized:

And also select and activate the options for hiding the panel:

Change the appearance of the panel in a tab Appearance:

Here you can customize the solid color, with a choice of color and transparency of the panel.
Adding applets to a panel
I already described adding a keyboard layout applet at the very beginning of the article. Other applets from the proposed default list are added in the same way. Right click on the panel, select Panel - Add New Items:

Removing applets from the panel
Removing applets from the panel is done as follows:
Right click on the applet and Delete:

4. Desktop customization
Right-click on any free space on your desktop and select from the menu that opens - Desktop customization:

In the window that opens Desktop three tabs: Background, Menu And Badges.

In the tab Background you can change the background image by clicking on it from the proposed catalog, or activate the option Change background at certain intervals, the desktop background images will change automatically, after a time set by the user.
Tab Badges is responsible for the appearance of the desktop. In it you can activate the display on the table Home folder, Trash etc. elements, as well as change their size and font size:

Tab Menu serves to configure the menu displayed on the desktop by right-clicking, or by clicking with the middle button (mouse wheel):


5. System settings
Settings systems you can find in Menu by clicking on the icon All settings:


System settings are divided into categories: Personal, Equipment, System And Other. All of them are already set by default, but you can change them at your discretion.
6. Additional programs to install
The system already has the necessary programs that the user can find in the menu. If you do not find any special program in the menu, then in the distribution kits Linux you don’t have to look for them on the Internet, first of all open them in the system menu Program Manager, most likely you can find the necessary additional software in it:

As you can see in the picture, all programs are divided into categories, which makes it easier to find the one you need. Click on the selected category and view the list of offered programs, or enter the desired name in the search field, click Enter on the keyboard, select the program, click on it and press the button Install:


7. Change window manager
Window Manager- A computer program that controls the placement and determines the appearance of windows in a graphical user interface window system.
IN Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce By default, several window managers are preinstalled.
Open All Settings - Desktop Settings:

And in the parameter Windows - Window Manager select the one you want to use. The manager will change on the fly:

Suppose a window manager has been selected Compiz. It already has some plugins for managing windows and desktop (Desktop Cube) activated:

Change settings Compiz can be pressed on the button Set up Compiz:

8. Installing additional programs on the desktop
Let's add some more goodies or frills to the desktop.
The bottom image shows two widgets: Conky and weather widget GisWeather.

And although the additions to both panels have their own weather elements, I think the widget is the most colorful and accurate for displaying the weather in your area GisWeather.
Installing the widget GisWeather
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gis-weather
Once the installation is complete, you will find GisWeather in programs Tools or search in the menu.
How to customize the widget and display your area, see.
Installation Manager Conky
Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), copy and run this sequence of commands:
sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install conky-manager
After installation you will find Conky Manager in programs Tools or search in the menu.
How to create your own widget Conky, look .
9. Install Skype
Skype- a free application that provides text, voice and video communication over the Internet between computers (IP telephony) and mobile devices, optionally using peer-to-peer network technologies, as well as paid services for calls to mobile and landline phones.
Program Skype is very popular among Internet users.

Installation Skype
Install Skype
sudo apt install skype
In system 64-bi T, Skype uses a theme Clearlooks instead of the default theme, other themes are also not displayed correctly.
This happens because Skype represents 32-bit application with theme GTK2, where is the engine Murrine in most cases it is not installed.
If you have installed 64-bit system, then fix the theme Skype you can by running the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt install gtk2-engines-murrine:i386 gtk2-engines-pixbuf:i386
Note. If after installation Skype You don't have a tray icon, just install one plugin. To do this, open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), and run the following command:
sudo apt-get install sni-qt:i386
And restart Skype.
10. Install Systemback - restore the system to a previous state
Systemback A very useful application that allows you to create backups and restore points of your system.

Peculiarities Systemback
System backup
System Restore
System installation
Creating a Live CD
System repair
System update
Installation Systemback
Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T), copy and run the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nemh/systemback
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install systemback
Instructions for use Systemback look .
Conclusion
These are the recommendations that I would like to offer at your discretion after installation Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce.
System Linux Mint 18 "Sarah" Xfce After installation and all the settings described above, it works stably, smoothly and looks very beautiful.
I have nothing against the Linux Mint logo and dark background, but it is more pleasant to work on the system when the desktop background is set to beautiful image. So first of all, let's change the background. Open Menu -> Options -> Wallpapers:
Then go to the Serena tab and select the picture you like. On the images tab you can upload your own:

2. Theme
Mint 18 also added the Mint-Y theme. It is made in a modern flat style and looks quite nice. You can activate it in the settings. To do this, open Menu -> Options -> Themes and select values for all parameters Mint-Y:

Looks quite nice.

3. Add widgets
Cinnamon supports widgets, which are called desktops here. Return to the main menu of the Settings utility and select Desclets:

Here you can add the desired widget to your desktop using the button Add to desktop:

Or install additional widgets from the network:

4. Update your system
It is important to keep your system up to date. Linux Mint has a special update tool, run it from the main menu:

When you first start it, the system will prompt you to choose which updates to install; it is recommended to leave it as is to get the new software:

Then you can choose necessary updates and press Install updates:

Most likely, you will need to do the procedure twice, since you may first need to update the update manager itself.

5. Installing codecs
Previously, codecs were supplied with the distribution and there were no problems with this. But then the developers decided to remove them. But we can install linux mint codecs from official repositories. For this we have an application center:

In the search, type mint-meta-codecs or just codecs, you will immediately see the package found, as well as its rating:

To open the package description window, double-click on it and then click Install for installation.
To install all available codecs, open a terminal and run the command:
sudo apt-get install gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly-amr gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly libgstreamer-plugins-bad1.0-0 gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad-videoparsers gstreamer1.0-plugins- bad-faad gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad libdvdnav4 libdvdread4
6. Install drivers
The system already contains drivers for many peripheral devices, even if they are closed source, But not all. For example, drivers for a video card must be installed separately. Open the driver manager through the main menu:
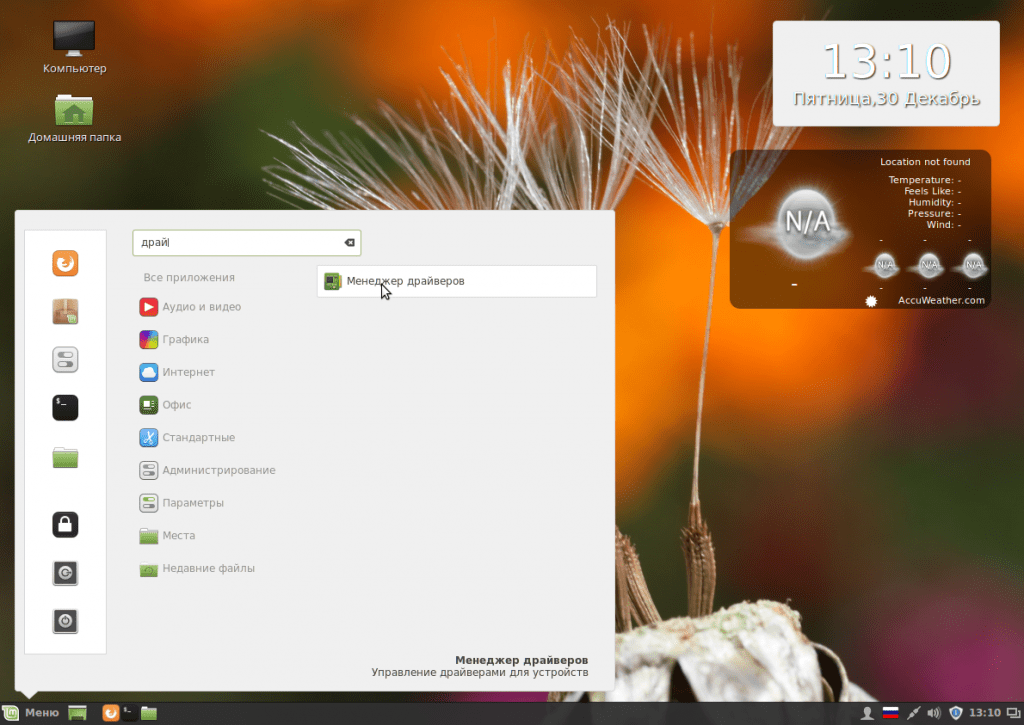
When the program loads, select the drivers you want to install and click Apply changes. After installing the driver, you will need to restart your computer.

7. Installing programs
Despite the fact that the system already contains many of the programs you need, not everything is there. Everything you need can be installed through the application center. Skype communication program:

VLC media player:

Audio player Clementine:

Graphic editor Inkscape:

Torrent client qBittorrent:

Aria2 Download Manager:

Mail client Mozilla Thunderbird:

Chromium browser:

BleachBit system cleaning program:

You can find and install others popular programs In chapter Favorites:

8. Installing Adobe Flash
Flash technologies are used less and less on websites, and are being replaced by HTML5, but many users still need Flash player. To install it, use the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install pepperflashplugin-nonfree
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure pepperflashplugin-nonfree
9. Install Java
Many programs require a Java machine to run. You can install it from the PPA repository. First add the repository:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
$ sudo apt-get update
Then install the package:
sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
10. System backup
Setting up Linux Mint 18 cinnamon after installation should include backup. While the system is still clean, you can create backup copy, so that you can quickly restore it later. To do this, you can use the TimeShift utility. First install it from the PPA:
sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install timeshift
Then launch the program from the main menu, then configure the backup frequency and create your first copy using the button Create:

Now you can restore the system if necessary.







