Search engine optimization. Internal ranking factors. Keywords in SEO optimization of articles
The term “website optimization” has recently been heard by many companies providing certain services in global network. But this is not surprising, given the enormous benefits that can be gained by properly building a strategy for advertising your products or services on the Internet. Let's first define the definitions and scope of the Internet audience that will be discussed in this article. I would like to emphasize that we will talk specifically about site optimization, without touching on such areas of Internet advertising as contextual advertising, media advertising, banner networks, advertising on thematic portals, spam (and, you see, it also has its place, although it is difficult call it an honest method of advertising), creating doorways, etc.
Website optimization (or search engine optimization) involves carrying out a set of measures to increase the visibility of the website in search results search engines(simply put, raising the site’s position) by a set of key phrases in search engines.
The most visited platforms for media advertising:
Rambler – about 3 million people per week;
Yandex – about 7 million people per week;
RBC – about 1 million people per week.
Well, the last definition that is worth mentioning in this article is website promotion, or its promotion.
By promotion we mean a certain set of measures to attract targeted visitors to a website on the Internet. It can be a combination in one quantity or another contextual advertising, search engine optimization, media, banner advertising and others legal ways Internet advertising, partially including design and programming work.
Based on this definition, we would also like to emphasize the fact that this article will focus specifically on optimizing the site exclusively for Russian-language search engines. This was done for the purpose that you cannot cover everything in one article, and there are quite significant differences between world search engines and Runet search engines.
What search engines does Runet have? Let's name the most popular of them:
Yandex, Mail.ru (currently broadcasting Yandex results), Rambler, Google, Meta.ua, Bigmir.net (currently broadcasting Yandex results).
Someone might also name Webalta or Aport, but we wouldn’t talk about the first one yet, since this search engine is only at the dawn of its activity and its future is still unknown. The second one is already fading away.
Based on the amount of transmitted search traffic (in Russia only), search engines can be ranked as follows:
Yandex ~ 60%
Rambler ~ 20%
Google ~8%
Mail.ru ~ 8%
… other.
Amount of transmitted search traffic in Ukraine:
Google ~40%
Yandex ~ 30%
Rambler ~ 18%
Mail.ru ~ 6%
Meta.ua ~ 3%
… other.
From this information we can conclude that when promoting a website in search engines, the user is most often interested in the search engines Yandex, Rambler, Google, Mail.ru, and Meta.ua to attract users from Ukraine.
I would like to immediately emphasize the fact that this dependence is not an axiom, and the amount of traffic attracted very much depends on many factors. Some of them: the subject of the site, positions in the search engine results, the description of the site provided by the search engine (the so-called snippet), the level of indexing of the site by the search engine (in other words, the number of pages of the site known to the search engine).
So, the main stages of search engine optimization of a website are:
1. Initial analysis of the field of activity, website analysis, competition analysis;
2. Selection of key queries for search engine optimization (compilation of a semantic core);
3. Work with the structure and content of the project;
4. Optimization of project metadata;
5. Work on the link popularity of the project (link exchange, registration in search engines, tops, directories, etc.).
These are perhaps the main stages of website promotion in search engines. However, it is necessary to talk in detail about each of them.
1. Initial analysis of the field of activity, website analysis, competition analysis.
At the first stage, an initial analysis of the company’s scope of activity should be carried out, carefully studying the structure of the site, its textual content, assessing the level of competition and, if possible, identifying the difficulties that will have to be encountered.
Perhaps this stage should be considered along with the compilation of the semantic core of the project, but let's dwell on real example determining the competition of a site selling household appliances and several units of goods for promotion through a search engine.
Let's say there is a website www.site.ru selling household appliances with units of goods in three areas: washing machines, microwaves, juicers.
What should you pay attention to?
Website construction
A good way to build the navigation structure of the site would be to separate these products into separate headings or folders on the portal, as well as placing the so-called general key queries (household appliances, buy household appliances, household appliances store) on home page portal (provided that emphasis is placed on promoting these requests).
For example, www.site.ru – requests for household appliances without reference to models or directions;
www.site.ru/washing/ - washing machines;
www.site.ru/microwave/ - microwave ovens;
www.site.ru/juicer/ - juicers.
A further hierarchy for the promotion of the project will be quite acceptable if, within each individual product area, there is a distribution according to the characteristics of the product itself, and then according to models.
For example, for washing machines:
www.site.ru/washing/ - washing machines;
www.site.ru/washing/bosch/ - washing machines from Bosch;
www.site.ru/washing/samsung/ - Samsung washing machines;
…
www.site.ru/washing/bosch/WVF2000/ - washing machine from Bosch, model WVF2000;
www.site.ru/washing/samsung/S1005J/ - Samsung S1005J washing machine.
I would like to emphasize the fact that the construction of the site may be different, but we will consider the most acceptable, in our opinion, general case for large-scale website promotion for a large number of search queries in search engines.
You can often find sites without text content on the main page or narrow specialization of companies. The main thing from this example is to understand the basic essence of the distribution of requests, namely, placing general requests that carry the comprehensive nature of the company’s activities on the main page, as well as dividing different areas of the company or online store into pages within the site with further distribution according to functional characteristics and model names.
This project structure allows, on the one hand, to facilitate the work of optimizing the project, and on the other hand, to complicate this process and extend the period of website promotion. But if you think globally, are focused on long-lasting results, and are not afraid of the test of time and difficulties in your work, we advise you to adhere to this particular strategy. Why - we will partially explain now, partially a little later (this concerns the internal link ranking of the site).
What do we gain with this distribution and construction of the site:
* Hit target audience to the page that clearly corresponds to the specified request (by setting the request “Samsung washing machine”, the user will go to the page www.site.ru/washing/samsung/, which fully satisfies his requirements). This indicator will also play a role in assessing the effectiveness of search engine optimization of the project. It’s no wonder that when using this key query on the main page of the site, or on any other, the user simply may not find the information he needs, after which he will close the page.
* Uniform, correct distribution of requests throughout the site. There is a hypothesis and a lot of debate about how many key queries to allocate per page. You won't find a clear answer, but it doesn't exist. Requests are different, so you need to think with the thoughts of a potential user who will come upon request to the page that you have planned. Let's take our example: a site with the page www.site.ru/washing/samsung/ for queries such as “Bosch washing machine” will look a little incorrect. Agree that this is not entirely true. And if there are more than one hundred key phrases, why not distribute them on one page? A correct approach to the problem is needed, and the scheme we propose completely solves it.
* Problem with the text content of the site. Looking ahead a little, let's say that the text content of a site is an important factor in its ranking by a search engine. Finding a key phrase is an important positive aspect for good positioning of a site in search engine results. It is very difficult to describe all the products or services on one page while maintaining conciseness and clarity of the information you want to convey to a potential client.
Many may say: “Yes, we have 5-6 requests, why separate them there, because we put everything on the main page.” Yes, perhaps this is how the question of time is resolved search engine promotion project, but not a question of the convenience of the user who comes to the site. It’s good if these queries are of the same root, and if the site has pages specially designated for this, why not use them?
Unfortunately, very often we come across such an opinion. For this reason, many companies, limiting themselves to 10-20 key expressions, display the main project page for the entire set. The result is poor returns from search engine optimization and wasted money. This may also not be entirely correct because when ranking a site, the search engine takes into account the “inclusion” of key queries in the text content of the page. Agree, sometimes it is very difficult to contain 10-20 different key phrases in the text on one page.
After we have carried out a preliminary analysis of the project structure, it would not hurt to conduct a small analysis of the site itself.
What to pay attention to:
* Writing robots.txt
The robots.txt file is used to prohibit certain search robots from indexing part or the entire site. The robots.txt file is located in root directory site and allows you to select a priority site mirror for some search engines (for example, Yandex) using the Host directive.
For more information on writing a robots.txt file, see: www.citforum.ru
* Using JavaScript,Flash
Search engines cannot always process JavaScript links correctly, so it is advisable to use them as little as possible. Website elements made in Flash are not indexed by many search engines. If a project's internal links are in Flash, most search engines will not find those pages.
* Generating a list of new pages or site map
Every time the site appears new page, it becomes known to the search engine only when the search engine robot finds it. If the page is located deep in the site, this may not happen soon. Placing a site map often solves the problem of site indexing and re-indexing.
* Dynamic pages
For several reasons dynamic pages poorly indexed or not indexed at all by search engines. We advise you to avoid dynamically writing website page addresses.
Competition Analysis
It is clear that when optimizing a project, we are interested in the first 10 positions in the search engine results. Therefore, we recommend that competition analysis be carried out based on the indicators of the first ten search engine results sites. First of all, you need to decide which search engine interests you. But due to the fact that the Yandex search engine generates the largest share of Runet traffic, let’s focus on the main indicators of the first ten sites that you should pay attention to first:
Pay attention to the PR indicators of the main and internal pages of the site, the TCI of the site, and also check its availability in the authoritative directories Yaca.Yandex.ru and Dmoz.org.
More details about TIC: help.yandex.ru
* Pay attention to the link popularity of the project and the presence of links from the main pages of the site.
This can be done using the command http://www.yandex.ru/yandsearch?Link=www.site.ru&iserverurl=www.site.ru. In Google, you need to set a search query like link:www.site.ru.
The search engine will display the number of links (not all) to the site and indicate the addresses of their location. When analyzing links to a site, it is important to pay attention to such indicators as: the topic of the links (the similarity of the topic of the linking site with yours), the presence of links from the main pages of other sites (again, pay attention to the topic of the sites, site authority indicators, the number of such links) , as well as the nesting of the page on which the link is located.
As a rule, the greater the number of links, the closer they are to the topic of your site, the higher their authority indicators, the higher the competition in this field of activity. It can be assumed that to achieve the same result, while maintaining a high level of site content, its construction, layout, graphics and other indicators, you will need in total approximately the same number of links to the site.
It will also be convenient for the Yandex search engine to check the number of sites that link to those that interest us, with certain content in the text of the page. This can be done using the command:
anchor#link="www.site.ru*"[key query] – links to the entire site as a whole with the content of the “key query”.
anchor#link="www.site.ru"[key query] – links to the main page (you can set the address of any other page) with the content of the “key query”.
This way you will also have additional opportunity assess the competition for individual queries by finding out the sources of links and the authority indicators of linking sites.
Unfortunately, direct queries in the Google search engine do not allow this. Look for this opportunity on webmasters’ websites, although the picture is quite clear from the statistics of the Yandex search engine.
Monitor the performance of all 10 or at least the first 5 sites from the top 10 search engine results. Carry out a cumulative analysis of those site authority indicators that you will focus on when promoting the project. From these same indicators, taking into account your capabilities and knowledge in the field of promotion, you can draw conclusions about the approximate timing of portal promotion.
After we have decided on the analysis of the site, area of activity and competition, we move on to the next stage - selecting key phrases to promote the project.
2. Selection of key queries for search engine optimization (compilation of a semantic core).
When selecting key phrases, we recommend using two services, namely: Yandex user query statistics - http://wordstat.yandex.ru/, as well as Rambler query statistics https://ad.rambler.ru/swrds/wrds.pl. On the left you will see key phrase, and on the right is the number of impressions of the request for the previous month. On average, the click-through rate (CTR), or in other words the number of transitions to the site, is 2-3%. Thus, you can calculate the approximate traffic that you will receive for a specific request if you get to the top of the search results:
Visitors = (Number of impressions*3%)/30 days per month.
I would also like to note that the number of visitors following a request directly depends on the position of the site, the so-called snippet (see below), the issued Title tag of the site, the popularity of the site and the relevance of the results.
Snippet is a description of the site displayed by the search engine when it appears. As a rule, this is a piece of text, or the content of the Description tag, which includes the searched key phrase.
Before promoting a website, it is important to determine for yourself what goals you are pursuing in the process of promoting the project - commercial or informational. Consequently, requests must be divided into commercial and informational.
In our case, commercial general queries for the main page of the site include (we ask the query household appliances in http://wordstat.yandex.ru/):
www.site.ru – main page
hardware store
online store of household appliances
sale of household appliances
chain of household appliances stores
home appliances website
household appliances company
buy household appliances
search for household appliances
TO information requests We also include:
Appliances
built-in home appliances
household appliances market
home appliances expert
home appliances electronics
small household appliances
household appliances forum
home appliances video
www.site.ru/washing/ — washing machines (we take only commercial ones)
washing machines
choose washing machine
buy washing machine
automatic washing machine
washing machine choice
sale of washing machines
ultrasonic washing machines
washing machines shops
best washing machine
built-in washing machines
www.site.ru/washing/bosch/ - washing machines from Bosch (we take only commercial ones)
washing bosch machine
bosch washing machines
Bosch washing machines
Bosch Siemens washing machines
Bosch washing machines
Bosch vertical washing machines
bosch washing machine price
Bosch washing machines
etc. (for simplicity and transparency, we will limit ourselves to these phrases in our example) These are not all the key phrases that are worth taking into account. But in order not to confuse the example and maintain some clarity, we will limit ourselves to only these phrases that are most popular among users.
I would like to note that the statistics also include queries like “bosch max washing machine”, “bosch 2460 washing machine”, but they already refer to specific models washing machines, for which separate pages are allocated according to the structure of our website. Therefore, these keyword phrases should be taken into account when optimizing the corresponding internal pages.
This analysis should be carried out across your entire product range by asking the queries “microwave ovens” (don’t forget about “microwave ovens”), “ washing machines", "juicers", etc.
Carry out a complete analysis and compile full list key queries for project promotion. Also pay attention to the right column in the selection statistics Yandex queries. This is what people who were searching for household appliances were still looking for. As a rule, queries in the right column are a good hint when selecting key phrases, often pointing to synonymous queries, or other queries on your topic that are interesting to the user.
When selecting key phrases, pay attention to abbreviations, queries with spelling errors, and the spelling of manufacturing companies in Cyrillic and Latin letters (for example, Samsung and Samsung). Simply put, when selecting keywords, you need to look at the task through the prism of your client's thinking, analyzing all the possible options for submitting queries when searching for a particular product.
Don't forget to look at your competitors and the keywords they use to promote.
If you expect quick results from search engine optimization, do not make a big effort to promote your project using single-word queries at the initial stage. Single-word keyword queries are often common, and greater popularity does not always indicate their huge commercial component. We also recommend paying great attention to highly targeted queries. In our case, these could be the queries “buy washing machines”, “buy Samsung washing machine”.
There is no need to further prove the fact that users who come to the site with the request “buy a Samsung washing machine” will be more desirable to you than users who come with the request “washing machines” if you are selling Samsung washing machines. However, this does not mean at all that you should not take into account the request for “washing machines”. We just want to emphasize that from the point of view of commercial returns, the second request will be much more practical, although less popular.
Assess your efforts to promote a project correctly, because sometimes the energy spent on promoting one strong request of the “household appliances” class can be directed to promoting 10 simpler, narrowly targeted requests (for example, “buy a washing machine”) and get a much greater return on promotion project, while spending less time and resources. As a rule, narrowly targeted requests are also quite simple to promote, which indicates another important aspect of promotion, namely the ability to achieve a fairly quick and stable result with a good commercial component.
The only problem when promoting a project for many narrowly targeted requests is their number. Of course, it is more convenient to promote 5-10 highly targeted queries than 100-200 small key phrases. But let’s think, first of all, about what goals we are pursuing, and also about the fact that a good quality website with good targeted traffic is not a task for one or two months. It can take years to resolve.
Most users on the RuNet get to sites through the largest search engines: Yandex and Google. But although both search engines set their main goal to generate independent results, there are a number of methods that allow a site to rise to higher positions in it, called SEO, search engine optimization or. In essence, both systems are identical, but there are differences between them.
So what is the difference between website optimization for Yandex and Google search engines?
Content. Search engines, both Yandex and Google, have a negative attitude towards non-unique texts on the site. But if in Google a site can be in the index even with unique content, then Yandex is less tolerant of plagiarism. Optimization of such a site is impossible; in addition, it may fall under a search engine filter (excluding some or all pages from the search results). Therefore, before you start promoting, you need to make sure that the resource contains a certain amount of unique content.
You can write texts yourself, entrust it to your employees, ask friends, or entrust it to specialists - copywriters who will do everything at the highest level. When contacting a specialized SEO company, website optimization for search queries will also include the work of professional copywriters.
As for the volume of articles, if you analyze the search results for one of the competitive queries, you will notice that all sites in Yandex will have texts that differ slightly in volume. Therefore, if you need optimization in this system, then you should pay close attention to this indicator, study competitors and take it into account when filling the site with material.
In Google, the volume of texts on sites in the TOP 10 can vary significantly: there may be resources containing landing page only tables, pictures or just some queries, as well as sites with a large amount of text. But this does not mean that you can’t pay enough attention to content when searching.
As for keywords (queries that users enter into the search bar), it can be noted that Yandex, as a system originally created for searching in Russian, is more flexible in this regard. Google is worse He is familiar with the morphology of the Russian language, for him it is very important that queries appear in direct occurrence. Therefore, if optimizing your site for this search engine does not produce results, it may be worth adjusting the texts and headings on the site.
But for both search engines, the interests of users are most important. And a resource that contains truly useful materials that respond to user requests will be much easier to optimize and achieve the necessary results.
Also, optimizing a site for the search engines Yandex and Google differs in relation to meta tags (title, description, keywords) and tags. There are several important points to highlight here:
- When optimizing a site for the Google search engine, you should pay attention to the direct inclusion of key queries in the title, especially for high-frequency and competitive words. For example, if a page is promoted for the query “metal door” and “metal doors”, then for Yandex it is enough to include one word form in the title, but in Google it may not reach the position without the direct inclusion of both word forms. Of course, this is not an axiom, but if website optimization in Google does not give the desired result, then you need to pay attention to this factor.
- Google in most cases takes content from the description to form a snippet, which cannot be said about Yandex. An attractive snippet is very important - based on it, users decide to go to the site. In addition, recent trends in SEO optimization indicate that the influence of behavioral factors on search results is increasing. That is, if users from a search engine either do not go to your site at all, or leave it after a few seconds of stay, its rating decreases and this will affect its positions. Therefore, when performing competent optimization, it is necessary to take this into account.
- The contents of the Alt tag are perceived differently by search engines. The American search engine takes it into account as the main text of the page, unlike the Russian one.
Optimizing a website for search engines is impossible without link mass. But search engines have different attitudes towards links. Google indexes links to the site much faster, so the effect of optimization appears faster. But this cannot be said about Yandex - the results from links can only be seen after some time, usually several months.
If an article contains several links to one url, then Google will count them as one, and Yandex will take everything into account. There are also differences regarding the location of links. It has been observed that Google often ignores links placed in the footer of a site, giving preference to links in the body text. Yandex counts everything.
As noted above, Google does not understand Russian morphology well, which is also true for link text - it is better that the bulk of the anchor list consists of direct occurrences of keywords. For Yandex, it is better to write the most natural anchor list, including various word forms. In addition, excessive occurrences of keys in a direct occurrence can cause a filter to be applied to the site (exclusion from the index).
It is worth noting that the influence of reference factors is also different. Website optimization in Google on the Russian-language Internet is still based on link mass, and with good links you can promote your website to the TOP, but for Yandex this is not so simple. With the introduction of Matrixnet, a decrease in the influence of the link factor can be observed, and this trend continues.
This means that successful website optimization for search engines must take behavioral factors into account. To do this, it is necessary to improve and develop the resource, in general, to approach this issue comprehensively.
And the last thing I would like to note about the description of the differences in optimization for both search engines is the frequency and features of updating their ranking algorithms. Google does not differ in the frequency of their changes, preferring to improve and improve the existing one. But Yandex never ceases to delight us with the release of new algorithms bearing the names of various well-known and not so famous Russian cities, the latest of which is Snezhinsk. Therefore, you must always be prepared for constant surprises on his part.
Of course, these are not all the discrepancies that exist in search engine optimization of a website under two largest systems. You can find out more in our other articles on our website. But to obtain a guarantee of high quality services and to be completely confident that your website will occupy the necessary positions in both Google and Yandex, you can only contact professionals in this field, which are the specialists of Artox Media Digital Group.
To promote your website, you first need to optimize it - make it attractive to search engines and users. If you adhere to some site optimization rules, this will help your project become popular and visited.
Determining the theme of the site
Decide right away why and for what you need a website. Choose the area in which you are most knowledgeable. There is no need to create a website with an undefined topic. Some resources contain sections dedicated to completely different topics, and this leads to a “blurring” of the overall theme of the site and a decrease in PR.
Remember: It is much easier to promote a site that talks, for example, only about website optimization, than one that talks about optimization, earnings, games, etc.
First of all, add unique content to your site (do not reprint materials from other sites). As the site develops, you will have to do this regularly. Avoiding repetition of existing materials, fill the site with truly high-quality content that is worthy of being cited by other sites. This is highly rated by search engines and users.
Website structure optimization
If you have a large website, break it up into thematic sections, sections into headings, etc. The result will be a structure in the form of a pyramid, where the main page will have more weight.
If the site is small, it is better to use a grid, where all pages are connected by links. Some people use both a grid and a pyramid.
URL optimization
It is better to create the names of pages and sections of the site using ones that are suitable for these pages in. For example, it would be more correct to name this page not "www..html", A "www..html". Search engines also take into account the presence of a query in the domain URL.
Text optimization
Place text content as high on the page as possible. Optimize your site so that the search engine that is looking for your content does not have to wade through a bunch of banners, tables, scripts, etc.
Don't put too much text or too little; search engines love medium-sized pages. Break the text into paragraphs to make it easier for visitors to read. Most users simply skim the page quickly, skimming paragraphs at a time.
Also, do not forget about keywords - they should appear at the beginning of the text (required), in the middle and at the end. Their density should be approximately 3-5%. Optimize your page for one or two words or phrases.
Tags h1-h6, strong and b, i, alt, title
The text must begin with a title placed in tags
. Be sure to use keywords in the title. Subheadings can be enclosed in tags
, etc., depending on their importance.
Several key words or phrases that appear in the text, especially at the beginning, are highlighted in bold ( or ), can be in italics ( ).
Provide images with an alt tag containing keywords. Use a description (title) in your links - this will be useful for users and search engines; you can also add keywords there.
Optimizing links
An important role in search engine optimization of a website is played by “anchor text” (the text content of the link). In the text of links, do not write “click here” or “here”, but insert keywords and combinations that correspond to the pages to which these links lead.
Meta tags
When optimizing a website for search engines, three meta tags are mainly used: title, description, keywords.
The most important thing is the title. This tag must be composed so that it includes keywords (required) and is attractive to the visitor, since this text will be visible in the search engine. Also check that the title of your page looks normal in the browser, in the list of bookmarks.
The second most important meta tag is description. Briefly describe what the page is about using keywords. And the more tempting this description is, the more likely it is that the user will go to your site.
Search engines once placed special importance on the "keywords" tag, but it is now largely ignored. Still, don’t forget to add a few of your own keywords and combinations to it.
- When optimizing your site, do not forget that you are creating it for users, not for search engines.
Information about website promotion and promotion is taken from the website
Introduction
This course is intended for authors and website owners who want to study in more detail the issues of search engine optimization and promotion of their resource. It is intended mainly for beginners, although experienced webmasters will hopefully learn something new from it. You can find a large number of articles on the topic of search engine optimization on the Internet; this textbook attempts to combine all the information in the form of a single, consistent course.
The information presented in this textbook can be divided into several parts:
— clear, specific recommendations, practical guidance for action;
— theoretical information that, in our opinion, any specialist in the field of SEO should have;
— advice, observations, recommendations obtained based on experience, studying various materials, etc.
1. General information about search engines
1.1 History of the development of search engines
In the initial period of Internet development, the number of its users was small, and the amount of available information was relatively small. In most cases, employees of various universities and laboratories had access to the Internet, and in general the Network was used for scientific purposes. At this time, the task of searching for information on the Internet was not nearly as relevant as it is now.
One of the first ways to organize access to network information resources was the creation of site directories in which links to resources were grouped according to topic. The first such project was the Yahoo website, which opened in April 1994. After the number of sites in the Yahoo directory increased significantly, the ability to search for information in the directory was added. This, of course, was not a search engine in the full sense, since the search scope was limited only to the resources present in the directory, and not to all resources on the Internet.
Link directories were widely used in the past, but have almost lost their popularity nowadays. The reason for this is very simple - even modern directories, containing a huge amount of resources, present information only about a very small part of the Internet. The network's largest directory, DMOZ (or Open Directory Project), contains information on 5 million resources, while Google's search engine database consists of more than 8 billion documents.
The first full-fledged search engine was the WebCrawler project, which appeared in 1994.
In 1995, search engines Lycos and AltaVista appeared. The latter has been a leader in the field of searching for information on the Internet for many years.
In 1997, Sergey Brin and Larry Page created Google as part of a research project at Stanford University. Google is currently the most popular search engine in the world.
On September 23, 1997, the Yandex search engine, the most popular in the Russian-speaking part of the Internet, was officially announced.
Currently, there are 3 main international search engines - Google, Yahoo and MSN Search, which have their own databases and search algorithms. Most other search engines (of which there are many) use in one form or another the results of the 3 listed. For example, AOL search (search.aol.com) and Mail.ru use the Google database, and AltaVista, Lycos and AllTheWeb use the Yahoo database.
In Russia, the main search engine is Yandex, followed by Rambler, Google.ru, Aport, Mail.ru and KM.ru.
1.2 General principles of search engines
The search engine consists of the following main components:
Spider is a browser-like program that downloads web pages.
Crawler (crawler, “traveling” spider) is a program that automatically follows all links found on the page.
Indexer is a program that analyzes web pages downloaded by spiders.
Database – storage of downloaded and processed pages.
Search engine results engine – retrieves search results from the database.
Web server (web server) – a web server that interacts between the user and other components of the search engine.
The detailed implementation of search engines may differ from each other (for example, the Spider+Crawler+Indexer combination can be implemented as a single program that downloads known web pages, analyzes them and searches for new resources using links), however, all search engines have the described general traits.
Spider. A spider is a program that downloads web pages in the same way as the user's browser. The difference is that the browser displays the information contained on the page (text, graphics, etc.), while the spider does not have any visual components and works directly with the html text of the page (you can do a “html code view” in your browser to see the raw html text).
Crawler. Selects all links present on the page. Its job is to determine where the spider should go next, based on links or a predetermined list of addresses. The crawler, following the links found, searches for new documents that are still unknown to the search engine.
Indexer. The indexer parses the page into its component parts and analyzes them. Various page elements are identified and analyzed, such as text, headings, structural and style features, special service HTML tags, etc. Database. The database is the repository of all the data that the search engine downloads and analyzes. Sometimes a database is called a search engine index.
Search Engine Results Engine. The results system is responsible for ranking pages. It decides which pages satisfy the user's request and in what order they should be sorted. This happens according to search engine ranking algorithms. This information is the most valuable and interesting for us - it is with this component of the search engine that the optimizer interacts, trying to improve the site’s position in the search results, so in the future we will consider in detail all the factors influencing the ranking of results.
Web server. As a rule, the server contains an HTML page with an input field in which the user can specify the search term he is interested in. The web server is also responsible for delivering the results to the user in the form of an HTML page.
2. Internal ranking factors
All factors influencing the position of a site in search engine results can be divided into external and internal. Internal ranking factors are those that are under the control of the website owner (text, design, etc.).
2.1 Text design of web pages
2.1.1 Amount of text on a page
Search engines value sites rich in information content. In general, you should strive to increase the text content of the site.
A page with only a few sentences is less likely to rank in the top search engines.
In addition, more text on the page increases the visibility of the page in search engines due to rare or random search phrases, which in some cases can lead to a good influx of visitors.
2.1.2 Number of keywords per page
Key words (phrases) must appear in the text at least 3-4 times. The upper limit depends on the total volume of the page - the larger the total volume, the more repetitions you can make.
Separately, we should consider the situation with search phrases, that is, phrases consisting of several keywords. The best results are observed if the phrase occurs several times in the text exactly as a phrase (i.e., all the words together in the right order), and in addition, words from the phrase appear in the text several times individually. There must also be some difference (imbalance) between the number of occurrences of each of the words that make up the phrase.
Let's look at the situation using an example. Let's say we optimize a page for the phrase “DVD player.” A good option is that the phrase “dvd player” appears in the text 10 times, in addition, the word “dvd” appears separately another 7 times, the word “player” another 5 times. All the numbers in the example are arbitrary, but they show the general idea well.
2.1.3 Keyword density
Keyword density on a page shows the relative frequency of the word in the text. Density is measured as a percentage. For example, if a given word appears 5 times on a page of 100 words, then the density of this word is 5%. Density that is too low will result in the search engine not giving due importance to the word. Too high a density can trigger the search engine's spam filter (that is, the page will be artificially lowered in search results due to excessive use of the key phrase).
The optimal density of key text is 5-7%. In the case of phrases consisting of several words, you should calculate the total density of all keywords that make up the phrase and make sure that it falls within the specified limits.
Practice shows that the density of key text is more than 7-8%, although it does not lead to any negative consequences, but in most cases it also does not make much sense.
2.1.4 Placement of keywords on the page
A very short rule is that the closer a keyword or phrase is to the beginning of a document, the more weight it receives in the eyes of the search engine.
2.1.5 Stylistic design of the text
Search engines attach special importance to text that is highlighted in one way or another on a page. The following recommendations can be given:
- use keywords in headings (text highlighted with “H” tags, especially “h1” and “h2”). Nowadays, the use of css allows you to override the appearance of the text highlighted by these tags, so the use of “H” tags is less important than before, however, they should not be neglected in any case;
— highlight keywords in bold (not in all the text, of course, but it won’t hurt to highlight it 2-3 times on the page). To do this, it is recommended to use the “strong” tag instead of the more traditional “B” (bold) tag.
2.1.6 TITLE tag
One of the most important tags to which search engines attach great importance. Be sure to use keywords in the TITLE tag.
As a rule, 50-80 characters from the TITLE tag are included in the search engine results, so it is advisable to limit the size of the title to this length.
2.1.7 Keywords in link text
Also a very simple rule - use keywords in the text of outgoing links from your pages (both to other internal pages of your site and to other resources on the network), this can give you a slight advantage in ranking.
2.1.8 Image ALT tags
Any image on the page has a special attribute “alternative text”, which is set in the “ALT” tag. This text will be displayed on the screen if the image could not be downloaded or the display of images is blocked in the browser.
Search engines remember the value of the ALT tag when parsing (indexing) the page, but do not use it when ranking search results.
At the moment, it is reliably known that the Google search engine takes into account the text in the ALT tag of those images that are links to other pages, while other ALT tags are ignored. There are no exact data for other search engines, but we can assume something similar.
In general, it is worth giving this advice - it is possible and necessary to use keywords in ALT tags, although this is not of fundamental importance.
2.1.9 Meta Desciption Tag
The Description meta tag is specifically designed to provide a description of the page. This tag does not affect rankings in any way, but is nevertheless very important. Many search engines (and, in particular, the largest Google) display information from this tag in search results if this tag is present on the page and its content matches the content of the page and the search query.
It's safe to say that ranking high in search results does not always result in a large number of visitors. If the description of your competitors in the search results is more attractive than your website, then search engine visitors will choose them rather than your resource.
Therefore, proper drafting of the Description meta tag is of great importance. The description should be brief, but informative and attractive, and contain keywords specific to the page.
2.1.10 Meta Keywords tag
This meta tag was originally intended to indicate the keywords of a given page. However, nowadays it is hardly used by search engines.
However, it's worth filling out this "just in case" tag. When filling out, you should adhere to the following rule: add only those keywords that are actually present on the page.
2.2 Site structure
2.2.1 Number of website pages
The general rule is the more, the better. Increasing the number of pages on a site improves its visibility in search engines.
In addition, the gradual addition of new information materials to the site is perceived by search engines as the development of the site, which can provide additional advantages in ranking.
Thus, try to post more information on the site - news, press releases, articles, useful tips, and so on.
2.2.2. Navigation menu
As a rule, any website has a navigation menu. Use keywords in your menu links to give extra weight to the pages the link leads to.
2.2.3 Keyword in the page title
There is an opinion that the use of keywords in the title of a page's html file can have a positive effect on its place in search results. Naturally, this only applies to English-language requests.
2.2.4 Avoid subdirectories
If your site has a moderate number of pages (several dozen), then it is better that they are located in the root directory of the site. Search engines consider such pages more important.
2.2.5 One page - one key phrase
Try to optimize each page for its own keyword phrase. Sometimes you can select 2-3 related phrases, but you should not optimize one page for 5-10 phrases at once, most likely there will be no result.
2.2.6 Home page of the site
Optimize the main page of the site (domain name, index.html) for the phrases that are most important to you. This page has the greatest chance of getting to the top of search engines.
According to my observations, the main page of a website can account for up to 30-40% of total search traffic.
2.3 Common mistakes
2.3.1 Graphic header
Very often, a website design uses a graphic header (header), that is, a picture that spans the entire width of the page, usually containing the company logo, name and some other information.
Should not be doing that! The top of the page is a very valuable place to place your most important keywords. In the case of a graphic image, this space is wasted.
In some cases, completely ridiculous situations occur: the title contains text information, but for the sake of greater visual appeal it is made in the form of a picture (accordingly, the depicted text cannot be taken into account by search engines).
It is best to use a combined option - the graphic logo is present at the top of the page, but does not occupy its entire width. The remaining part contains a text title with keywords.
2.3.2 Graphical navigation menu
The situation is similar to the previous point - internal links on your site should also contain keywords, this will give an additional advantage in ranking. If the navigation menu is made in the form of graphics to make it more attractive, then search engines will not be able to take into account the text of the links.
If it is not possible to abandon the graphical menu, do not forget to at least provide all images with the correct ALT tags.
2.3.3 Navigation via scripts
In some cases, site navigation is carried out through the use of scripts. It should be understood that search engines cannot read and execute scripts. Thus, the link specified through the script will not be available to the search engine and the search robot will not follow it.
In such cases, you should definitely duplicate links in the usual way so that site navigation is accessible to everyone - both your visitors and search engine robots.
Hello, dear readers!
Do you put your whole soul into writing an article for your online information resource?
And the article not only doesn’t make it into the TOP 10 of search results, but also barely makes it into the top 100 for a given query?
Yes, the picture is sad, but fixable!
Today you will learn how to optimize articles for search queries so that they never fall behind again.
From now on, your materials will not only appear in the top ten search results, but also the TOP 3 for them will be quite possible.
Keywords in SEO optimization of articles
Have you heard of such a concept as a semantic core? How to compose it?
If not, then let me explain to you.
The semantic core is a set of search queries in all their word forms (number, case), which reflects the need regular user in the required information.
To identify the most relevant and competitive search queries on a specific topic, you need to use special services, which reflect user queries in search engines.
The simplest and most accessible service for these purposes is the Yandex.Wordstat service https://wordstat.yandex.ua/
Let's look at the example of this article to see how keywords were selected for it using this service.
Since my goal was to write material on the topic proper optimization articles for the site, in the Yandex.Wordstat line I entered the main phrase “article optimization”, and this is what I came up with:

As can be seen from the screenshot, this phrase is entered by users into search bar Yandex on average 1110 times per month (including additional words).
The left column displays search queries with the specified phrase, and the right column displays the number of their impressions per month.
And to find out how often articles with a given query in this word form (that is, number and case) are shown in search results, I put the phrase under study in quotation marks and placed it in front of the words exclamation marks, like this:

From the screenshot it is clear that the search query “article optimization” has a low frequency - 16 impressions per month.
Therefore, the article cannot be limited to just one such key phrase. You also need to use the clarifying queries that were given in the screenshot above.
In addition, I decided to check the frequency of a phrase with a verb (a word with the same root) and the particle “how” (which Russian-speaking users love to use in their queries). Here's what happened:

The Wordstat service showed that users specify such a query in the Yandex search engine about 302 times per month (this includes clarifying queries).
And the query itself “how to optimize an article” in this word form has a frequency of 16 impressions per month:

The same number of impressions came out as in the first case.
Therefore, I decided to use these two key phrases in my article, as well as queries that clarify them (after all, they also have impressions, and therefore there will be transitions).
Another technique for increasing article traffic from search engines is to use synonyms for key phrases.
Using a dictionary of synonyms can significantly increase your semantic core.
Unfortunately, for the topic of this article, I could not use this method, since I did not find synonyms for the word “optimization.” Maybe someone can tell me? 🙂
As a result, I came up with this semantic core for this article:

Thus, I have given you an example of optimizing an article on a website using keywords.
After analyzing the key phrases on your topic, you just need to correctly distribute them throughout the text of the article, in headings and subheadings. But this is a completely different story, which will be discussed in the material on how to write optimized articles.
Optimizing articles for search engines
It is possible that your article is not as hopeless as you think. Maybe it still has clicks from search engines, and from time to time it appears in search results.
To find out what queries are used to find your article, Google Analytics (https://analytics.google.com/) and Yandex.Metrica (https://metrika.yandex.ua/) services will come to your aid.
I hope you already have accounts in these services in order to view and analyze information on transitions to your site over the past period.
Working with Google Analytics
In order to view which key queries your articles are displayed in search results, you need to go to the following tabs in the left menu Google service Analytics:
Traffic Sources -> Search Console -> Queries

Now in the window that opens on the right top corner You must select a date range. If you have not previously carried out such an analysis, I recommend indicating the period for the last 3 months (more is possible).

Below you will see a line graph of statistics on clicks (can be configured for other positions) - that is, transitions from the search engine Google systems for key queries on your website. But for our purposes we will not need such information.
The table columns will display:
- search queries that led to your articles being shown in search engines;
- number of clicks on articles on your website as a result Google search(in the corresponding cell in the table header there is a downward arrow, after clicking on which the output will change this parameter from its smallest value to its largest);
- number of impressions by article as a result of the search;
- CTR, which is in this case reflects the percentage of transitions to your website for a specific key query in the Google search bar;
- average position (rating) of your article according to queries. For example, if a certain article is in 5th place in search results for one query and in 7th place in another, then the average position will be 6.
By default, the table shows only 10 search queries with the largest number clicks For ease of work, it is better to immediately change the number of its rows, using the settings for their display, which are located under the table in the lower right corner.
Also here you can find out how many total search queries are presented in this report for the specified period (in my example it is 2640) in order to correctly select the number of rows to display them on one page. In my case, from the drop-down list I select their maximum number - 5000 lines.
Now you see the whole picture - all search queries for which Page URL(article) of your website for the specified date range.
With the data obtained from the table, you will have to work to optimize the site’s articles.
- a significant number of impressions during the reporting period,
- CTR is less than 10%,
- high number of the middle position (from 6 and above).
Look at the first column with the queries that users use to find articles on your resource.
If you see key phrases in the list that you haven’t used in your materials, but they have a significant number of impressions and a small number of clicks, then it makes sense to add these phrases to feature articles.
Identify search queries that have 3 of these characteristics:
To increase the position of your articles for such queries in search engines, they will need to be included in your thematic texts.
Even if they are already present in such a word form, they will need to be repeated again (this will increase their density).
When optimizing articles using this scheme, make sure that your materials do not become overloaded with key phrases. They should be used only where they are truly appropriate and will not “break” speech patterns and set expressions.
Remember not only the positions of your articles in search engines, but also the readers.
Working with Yandex.Metrica
To find out what key queries search engine users use to find materials on your website, you can use a service such as Yandex.Metrica. It has some differences from the previously reviewed Google Analytics. Next you will see it for yourself.
In my opinion, this service is more democratic than other search engines and displays more reliable information.
So let's get started.
Login to your account Metrics and follow the following path through the tabs of the left menu:
Reports -> Standard reports -> Sources -> Search phrases


After clicking the “Apply” button, a line graph is displayed by default on the page, which displays, point by point, the number of visits for the most popular search queries for the reporting period.
In addition, for greater clarity, user visits for these key phrases can be displayed in the form of a pie or bar chart.

This is a very interesting solution, I think. You visually see for which queries your site is most popular, and immediately draw a conclusion about which articles have the highest positions in search engines.
Below the graph is an analytical table of search phrases with the following columns:
- The first column shows the name of the keywords, as well as the icon of the search engine from which the request came.
- The third column indicates the number of unique visitors for these key phrases, which can also be sorted by a specific value, as well as converted into a percentage.
The second column reflects the total number of visits for the corresponding request for the specified period.
By default, all keywords are sorted by quantitative value this indicator(to decrease).
And when you click the down arrow, the table data will be rearranged from a lower value of a given column to a larger one.
In addition, the funnel-shaped button makes it possible to sort the visit indicator from a specific value up or down.
And the button in the form of “%” allows you to show percentage visits for a given search query relative to transitions to the site for other queries.
The “Bounces” column reflects the share of transitions to a site whose stay on the page was less than 15 seconds.
And this failure rate must be reduced to zero.
The visitor needs to be “detained” on the site, attracting his attention to other articles.
And then the value of the coefficient given in this column, will increase.
The last column shows the average time of a visit to the site for a key query.
Work should be done on this indicator aimed at its growth.
As you can see, the Metrics analytical table for search phrases differs in its quality content from a similar table in Google Analytics. Its indicators are aimed at analyzing and solving other issues.
How can you use this data to correct seo article optimization?
First of all, just like in the case of a table in Google Analytics, study the search queries from the first column and identify those that are not in this entry in your articles.
If the request matches the topic of your material, write it into the text of the article.
And if the request specifies a qualifying word (for example, the word “download”), and your article does not provide such a function, then there are 2 solutions - either skip this request altogether, or add to your material by including this feature.
Look for keywords with a high bounce rate (more than 5%) and a time on site of less than 1 minute.
Make sure that the content of the article with this search query has a solution of this request and satisfies the user's needs.
If the topic of the article is not fully covered, it is worth adding to it in order to keep the visitor on the site.
To increase the viewing depth, in the text of articles, use internal links to other articles on your resource.
Make anchors by writing down the key phrases of these very other articles.
Search engines approve of this.
Just please don’t overdo it with their quantity. You shouldn’t put internal links in almost every sentence.
They should be distributed evenly throughout the text.
For an article of 10 thousand characters, bp. (without spaces), 5-6 internal links in it will be the optimal solution.
Meta tags in optimizing a website article for search queries
The work doesn’t end with editing the texts of articles to optimize them for SEO requests.
The next step is to analyze and adjust the meta tags.
The H1 header, Title and meta-description should contain the main key phrases of the article.
Let's sort it out in order.
Heading H1
- This is the title that is displayed on the article page and is user-oriented.
It must include the main key phrase (preferably at the beginning of the title).
A good example is the title of my article.
You cannot put periods, ellipses, or exclamation marks at the end of the title.
Only a question mark is allowed if the search query begins with the words "how", "why", "how much", etc.
There are no particularly strict requirements for the length of the H1 header.
Title Title
- This title is especially important in the internal context, because it is what is displayed in the search results.
- The Title header is the name of the site page, which is reflected in the browser tab.
- It should reflect the content of the article as succinctly as possible, which means it should include the main key and words complementing it. Numbers and words that encourage action are also welcome (if they are appropriate, of course).
- Dots and exclamation marks are also not allowed at the end of the title; only a question mark is allowed.
- The optimal length for Title is 60-65 characters (including spaces).
- The description meta tag is displayed as a result of the search, so it should briefly describe the content of the article and the issues that are addressed in it.
- The description must include the main key phrase of the article, and it is advisable to write it at the beginning (in the first 100 characters).
- The ideal length for description is two lines of 2-3 sentences (150-160 characters without spaces).
The role of images in article SEO optimization
Surely you used images to make it beautiful.
But novice bloggers often make mistakes when choosing pictures and uploading them to the site.
The first mistake newbies make is borrowing someone else’s photos and posting them on their website.
- Search engines may regard this action as plagiarism and not display your articles in their results.
In addition, you risk being caught by the author himself of stealing his property.
He may initiate legal proceedings on grounds of copyright infringement.
Do you need this?
To avoid such problems, you can do two things:

Image optimization
The second mistake novice bloggers make when working with images is that the selected images are uploaded to the site in the same form. But they can have a huge expansion and a significant size in kilobytes (megabytes).
Such “heavy” images prolong the loading time of the website page by the browser. And the page loading speed indicator is one of the most significant for both search engines and users.
Set right size pictures for its correct display on the article page will not be difficult. This can be done using any graphic editor(including the online editor).
But to reduce the weight of the image in KB for it fast loading on the article pages you must use special programs or online services.
I'll show you how it's done in Adobe Photoshop:
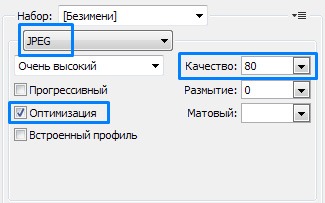
If you are completely unfamiliar with Adobe Photoshop, you can use image optimizers that require installation on your computer. But there are also online versions:
- https://tinypng.com/
- http://tools.dynamicdrive.com/imageoptimizer/
Name of images on the site
And the last third mistake when working with images is the incorrect spelling of their names for uploading to the site. In addition, novice bloggers often ignore such attributes of the uploaded image as alt and title.
You need to give the image a name:
- in Latin letters (to translate Russian name into Latin, use the service http://translit.net/);
- without punctuation marks or other special characters;
- writing lines between words.
An example of such a name is “kak-optimizirovat-stati”.
In the title of the main image for the article, you need to use the main key phrase, and in the title of the images that are placed in the body of the article, it is recommended to use complementary search queries.
If the image is a screenshot, graph or diagram, then you should give it a name that matches its content.
Webmasters have different opinions regarding filling out the alt and title attributes of an image.
- Some people think that the title attribute is useless, others insist on its importance.
- Some write alt and title the same way, while others are sure that these attributes should be written differently.
- Some believe that these attributes should be written in Latin, like the name of the image, while others write them in the language in which the article is written.
However, everyone agrees that the alt attribute is required, since it describes the image, and this information is read by search engines.
Personally, I adhere to the following rules when filling out the alt and title attributes to optimize images on the site:
- I write alt in Latin, like the name of the picture, leaving dashes between the words.
- I always fill out the title attribute, writing it in Russian letters according to the name of the image.
Thus, the content of the attributes pictures alt and the title is repeated, but written in different letters.
This concludes the topic of how to optimize articles for search queries. I hope that you have learned a lot of new and useful information and you will use it in the development of your resource.
In the comments, share your successes and experience in optimizing articles on your site.
Or perhaps you use other tools and methods for these purposes? I think everyone will be interested to know about them.
Also, if you have any questions regarding certain points discussed in the article, leave them in the comments.
Thank you all for your attention! See you again!







