We find out the reasons why the BIOS does not see the hard drive. BIOS does not see the hard drive BIOS does not see the hard drive
If you turn on your PC and its BIOS does not see the SATA hard drive, then, despite the fact that this situation, of course, cannot be called pleasant, in some cases it can still be successfully resolved. However, the methods for solving the problem and the likelihood of success largely depend on the causes of the malfunction, of which theoretically there can be several.
Hard drives have long taken leading positions in the field of long-term information storage as devices that combine high capacity, low price and acceptable reliability and speed characteristics. While hard drive technology may not have advanced at the same rate as other computer components such as the processor and memory, hard drives today are far superior to their predecessors in terms of capacity and speed. In the last decade, significant progress in improving the parameters of hard drives was largely associated with the transition to a new technology for exchanging data between the hard drive and the motherboard -. Currently, SATA hard drives have practically replaced hard drives with an IDE interface from use, largely due to their high speed and the absence of limitations typical for IDE drives. In particular, connecting SATA hard drives to a computer is much easier and faster compared to IDE drives.
However, users of drives with a SATA interface are not immune to problems. There is often a situation where the hard drive is not visible to the old operating system. But a particularly unpleasant problem is that the hard drive is not recognized at the BIOS level. In such a case, naturally, this hard drive cannot be used to store data; In addition, it is impossible to boot a personal computer from it.
There may be several reasons for the situation when the BIOS does not see the hard drive, but basically they can be divided into the following categories:
- Hard drive or motherboard failure
- Error connecting the drive
- Error when setting BIOS options
Errors when setting BIOS options and fixing them
Many BIOS have a number of options that allow you to configure the operating parameters of the SATA host controller built into the motherboard chipset. In some cases, incorrectly setting the values of such options can lead to the inoperability of all or some of the hard drives connected to the computer, or to the inoperability of certain types of them, for example, drives connected to IDE or SATA connectors.
In particular, the option found in some BIOSes has the value PATA Only, which disables support for SATA hard drives, leaving only IDE interface drives for use. In addition, if the controller in the BIOS is configured in such a way that it supports the traditional mode of accessing drives in IDE mode, then in this case the system can support no more than 4 drives, and all extra drives will simply not be visible.
Sometimes it happens that the BIOS does not recognize the second SATA hard drive installed in the system. In this case, the problem may be either a BIOS error or the fact that the SATA drives belong to different versions of SATA, for example, the first is SATA-2, and the second is SATA-3. In this case, it is best to set the second hard drive to SATA-2 operating mode using the corresponding jumper on its case.
Some options, such as Serial-ATA Controller, allow you to disable the SATA controller altogether. In this case, all drives connected to the motherboard connectors will not work.
You should also note that in some BIOS you can disable automatic detection of hard drives. Check if you have such an option, and if so, then its value should be set to Auto.
Additionally, in some cases, especially with older motherboards and BIOS, there may be errors in the BIOS that prevent the system from recognizing the hard drive correctly. To eliminate this possibility, you need to reset the BIOS to default settings, and if the BIOS still does not see the disk, then update the computer's BIOS version.
Errors when connecting drives to the motherboard, physical malfunction of drives and other components of the system unit
SATA hard drives do not require jumper settings to select Master and Slave operating modes, which are vital for the operation of IDE drives, so their configuration in the system is not required. In addition, SATA connectors and cables are much more convenient than IDE connectors and cables, and therefore most users do not have any problems connecting SATA hard drives. However, insufficiently tight contacts between cables and sockets can also lead to a situation where the BIOS does not see the SATA hard drive installed in the system. If you have made sure that the controller configuration in the BIOS is configured correctly, but the BIOS still does not see the disk, it makes sense to check the reliability of the cable connections to the motherboard, and also check the cables themselves by replacing them with other cables of the same type.
If after this check procedure the BIOS still does not see the hard drive, then it makes sense to check it in another place, taking a second system unit - it is quite possible that the problem lies in the hard drive itself - in the disk controller or in the mechanical drive. In the first case, the disk can most likely be repaired; in the second case, you will have to look for a replacement.
In some cases, the problem may not be with the hard drive, but with the SATA host controller on the motherboard. If this is the case, then the motherboard will most likely need repair. There are also cases where the BIOS does not see hard drives due to a faulty power supply.
Conclusion
The situation when the BIOS of a personal computer does not see one or more hard drives operating using the SATA interface, fortunately, does not occur very often. However, a similar problem may occur, especially if the computer is using an old version of the BIOS that contains errors, or if two SATA drives belonging to different generations of SATA are simultaneously installed in the system (in such a case, the second the disk may not be detected). Also, in some cases, there may be incorrect settings of BIOS options, incorrect or careless connection of disks using data or power cables. The user is not immune from hardware failures in the operation of the disk controller, as well as in the operation of the SATA host adapter located on the motherboard. In the latter cases, the problem can be corrected, as a rule, only by contacting the service center specialists.
The problem where the hard drive is not detected by the computer is quite common. This can happen to a new or already used, external or built-in HDD. Before you try to fix the problem, you need to figure out what caused it. Usually, users themselves can fix difficulties associated with the hard drive - to do this, just follow the instructions and act carefully.
There are several common situations that can cause a hard drive to fail to perform its function. This applies not only to a disk connected to the computer for the first time - one day the main HDD may stop working, making loading the operating system impossible. These reasons may be:
- First connection of a new drive;
- Problems with the cable or wires;
- Incorrect BIOS settings/failure;
- Weak power supply or cooling system;
- Physical failure of the hard drive.
In certain cases, you may encounter the fact that the BIOS sees the hard drive, but the system does not. Accordingly, a less experienced user may have difficulty diagnosing and fixing the problem. Next, we will analyze the manifestation and solution of each of them.
Reason 1: Connecting the drive for the first time
When a user connects an external or internal hard drive for the first time, the system may not see it. It will not appear among other local disks, but it is physically fully functional. This is easy to fix and should be done as follows:

Even if the utility "Disk Management" does not see the equipment, use alternative programs from third-party developers. Our other article at the link below describes how to format using special applications designed for advanced work with HDDs. Use Method 1, which covers working with different software.
Reason 2: Invalid format
Sometimes the disc does not have an item "Change drive letter or drive path...". For example, due to a mismatch in the file system. To work properly on Windows, it must be in NTFS format.
In this case, it must be reformatted to become accessible. This method is only suitable if the HDD does not contain information, or the data on it is not important, because all data will be deleted.

Reason 3: Uninitialized HDD
A new and unused hard drive may not work immediately when connected. The hard drive does not initialize on its own, and this process must be done manually.

The disk will be initialized and ready to use.
Reason 4: Damaged connectors, contacts or cable
When connecting external and internal hard drives, you need to be careful. The external HDD may not function due to a damaged USB cable. Therefore, if there are no visible reasons why it does not work, then you should take a similar wire with the same connectors and connect the drive to the computer. An internal hard drive can also have this problem - the cables have failed and need to be replaced for the drive to work.
Often, simply reconnecting the SATA cable to a different connector on the motherboard often helps. Since there are usually a sufficient number of them, you will need to connect the SATA cable to another free port.
Due to inattention or insufficient experience, the user may incorrectly connect the hard drive inside the system unit. Check the connections and make sure the pins are not coming loose.
Reason 5: Incorrect BIOS settings
The computer does not see the system disk


The BIOS may not be set to an IDE-compatible operating mode.

BIOS does not recognize the hard drive
Usually, even if the BIOS does not detect the hard drive, it is due to incorrect settings or their failure. Incorrect settings appear as a result of user actions, and failure can occur for various reasons, ranging from power outages to viruses in the system. This can be indicated by the system date - if it is not accurate, then this is a direct indicator of a failure. To fix it, you need to do a full reset and return to factory settings.

Outdated BIOS
When you try to connect a new drive to a too old computer with the same BIOS, you sometimes cannot avoid problems. This is due to software incompatibility and outdated control files. You can try to update the BIOS firmware manually and then check the HDD visibility.
Attention! This method is intended exclusively for experienced users. You will perform the entire process at your own peril and risk, since if you do it incorrectly, you can lose the functionality of your PC and spend a lot of time restoring its functioning.
Reason 6: Insufficient power or cooling
Listen to the sounds coming from the system unit. If you hear the buzzing sounds of cycle changes, then the culprit is most likely a weak power supply. Act according to the circumstances: replace the power supply with a more powerful one or disconnect a device of secondary importance.
If the cooling system does not work well enough, then due to overheating the disk may periodically cease to be detected by the system. This most often happens when using a laptop that usually has weak coolers that do not do their job properly. The solution to the problem is obvious - purchasing more powerful cooling.
Reason 7: Physical failure
Due to various reasons, the hard drive may fail: shock, fall, impact, etc. If the above methods did not help, then you should try connecting the HDD to another computer. If it is not detected by it, then, most likely, this cannot be corrected at the software level, and you will have to find a service center for repair.
We looked at the main reasons why a hard drive does not start. In fact, there may be more, since it all depends on the specific situation and configuration. If your problem has not been resolved, then ask questions in the comments, we will try to help you.
When you turn on your computer, the BIOS checks its hardware. This also applies to hard drives. The BIOS does not see them if the hard drives are physically damaged. In this case, a message appears on the monitor indicating this. Some of the most serious problems can only be solved by specialists, but some of them can be solved by any user.
Most common reasons
If the hard drive is not visible in the BIOS, the reasons may be software failures or hardware failures. The most common of them are the following:
- incorrect setting of jumpers on the hard drive;
- its connection is incorrect;
- hard drive damage;
- disabling it in the BIOS.
These reasons are mainly characteristic of HDDs, but to some extent they also apply to SDDs. Below they will be discussed in more detail.
Incorrect hard drive connection
If the BIOS does not see the hard drive, the problem may be that it is not connected correctly to the motherboard. To eliminate it, you need to remove the protective casing from the system unit and check the connection of the hard drive cables. Remember that if the connection is incorrect, the hard drive will not be visible in the BIOS. SATA cables often fall out of their connectors, so you need to check that they are securely fastened. The length of such a cable should not exceed 1 meter. If ATA UDMA cables are used, their length should not exceed 45.72 cm.

Their connectors have different colors, which must be positioned correctly when connecting:
- black is used for master devices;
- gray - for subordinates;
- blue - to the motherboard.
Jumper settings
It is relevant for IDE disks. In this case, the BIOS does not see the hard drive when, due to jumpers, the primary and secondary hard drives are incorrectly determined. To do this, you need to turn it over and look at the Master and slave drives image on the label.
On SATA drives with a speed of 3 Gbit/s, it may not be detected by the controller with a maximum speed of 1.5 Gbit/s, and therefore this parameter on the hard drive must be reduced to these values. For some ATA drives, you can set the jumper parameter “Detected by cable”.

If the jumpers have been subjected to oxidation, you can deal with them as follows:
- treat with an anti-corrosion solution intended for these purposes and sold in specialty stores;
- clean with sandpaper, and special care must be taken - one careless movement will lead to the fact that the hard drive will have to be replaced.
Checking settings
If the system was completed incorrectly, then the BIOS does not see the hard drive on the computer because it made changes there on its own. Therefore, you need to check its settings. On different computers, entering there is done by pressing different keys, usually F2 or Del. If the BIOS does not see the SATA hard drive, go to the Main section, and then to the Sata Configuration parameter. The value is set to Enabled. After that, save the changes by pressing F10 and reboot the computer.
In addition, booting from the hard drive may not occur if it is not the first boot device. Also, the BIOS may not detect the hard drive if it is infected with viruses. You can try resetting all settings by resetting them to factory settings.

This action can be performed through the BIOS itself, as well as in other ways:
- The computer turns off.
- The power cord is removed from the outlet.
- On the motherboard there is the inscription Clear CMOS with a jumper mounted on a three-pin connector. In the working position it stands on contacts 1 and 2. It is removed and they are rearranged 2 and 3. After 20-30 seconds they are returned to their original position.
You can also reset the BIOS by removing the battery, waiting at least half an hour and putting it back.
Checking for serviceability
If the BIOS does not see the hard drive on the laptop, you need to check if it is overheated and remember if this gadget has crashed recently. The disk, OS, or laptop itself can become unusable over time. You can check the serviceability of the first one by connecting it to another device. If it is not recognized, you need to buy another hard drive. When working on a laptop, you need to keep in mind that it should not be placed on soft and uneven surfaces; free access of air for the cooling system should be provided through its ventilation holes.

Defects are identified during a visual inspection. The following may be found:
- malfunction of some parts;
- defects in the outer casing;
- Damage to chips on the hard drive board.
Problems with the motherboard
The north or south ports may fail or the contacts that are necessary to connect to the hard drive may burn out. In this case, the user himself is unlikely to be able to understand the reasons. Qualified professional help is required. Therefore, if you don’t know how to get the motherboard, a laptop or computer is taken to a service center. To avoid problems with it, you need to check its connectors and the hard drive for misaligned contacts or bends. You need to connect one hard drive per cable.
Lack of nutrition
This problem may occur after upgrading your computer, or if you install a weak power supply. When purchasing a computer, it is better to plan to equip it with an appropriate device with a power reserve, so that in the future you can painlessly upgrade the main components. If there is insufficient power supplied to the disk, it will not spin.

To determine whether this is the reason why the hard drive is not detected by the BIOS, you need to take the following steps:
- Turn off computer.
- Remove the casing from the system unit and disconnect the hard drive cable.
- Turn on the computer. Rotation is checked by light vibration emanating from the side of the hard drive. If it is not felt or heard, it is not running.
- Connect the power cables to the CD or DVD drive. This will let you know whether they are working or not.
- The power supply is checked to ensure that it produces the required power.
- If the disk does not start spinning, you need to check it on another device.
- The test can be performed on a special SATA-USB case.
- If all these actions do not lead to the disk starting to rotate, you need to take it to a service center under warranty or for post-warranty service.
Manufacturing defects and physical malfunction
Conventional hard drives quickly become inoperable if damaged slightly. In this regard, ASUS BIOS does not see the hard drive, as well as other laptops. The cause may be a shock, impact or fall. The following may happen:
- magnetic plates are damaged;
- engine bearing jams;
- magnetic heads stick.
In this case, the user will not be able to cope with the problems that have arisen on his own; he needs to seek help from professionals.

In addition, severe overheating can lead to loss of the hard drive. As a result, the board may fail, which will also require specialist intervention. If you bought a new hard drive at the store, but the BIOS does not see the hard drive, then, most likely, they sold you a defective one. Therefore, if the warranty is still valid, it is better to take it to a store or service center. Remember that if you intervene on your own, the disc will not be accepted under warranty. It is necessary to purchase hard drives from those retail outlets that you trust and where you have already made purchases.
Finally
As part of this article, it was determined why the BIOS does not see the hard drive. This may be due to the fact that it is faulty for a physical reason, or because of a manufacturing defect, or because the computer was upgraded, as a result of which the power supply became insufficient. Also one of the reasons may be problems with the motherboard. The disk may be faulty or the jumpers are set incorrectly. In addition, when opening/closing the system unit, you can touch the cables, which will cause them to be disconnected from the power supply or the motherboard. Also, the disk may be disabled in the BIOS, or its settings may be incorrect.
At the moment, this device is the most necessary and relevant for storing memory. However, many often encounter such a problem as “the laptop BIOS does not see the hard drive.” The BIOS is responsible for controlling the motherboard and the devices connected to it.
Hard drive is a system, which stores information and is responsible for the functionality of the software.
Main reasons for lack of connection

The first thing you need to do is check the connection of the ATA or SATA ports, as well as their automatic configuration.
If everything is fine with the ports and they are working properly, then you can find out why it is not displayed using the following steps:
- Check the connections of all components.
In order to determine the true cause, you need to make sure that all elements are connected correctly. You need to look at the location of the cable and motherboard, as well as their serviceability and integrity.
If everything is in order with these devices, you need to pay attention to other elements; perhaps they could cause a failure in the BIOS.
- Check the serviceability of the jumpers.
Jumpers are sockets, to which all cables and wires are connected.
If the problem is in the jumpers, then you can fix it in the following ways:
- very carefully treat the surface, removing rust;
- Clean the jumpers with sandpaper, but you must be very careful and careful.
If the steps taken do not help, then you should contact a specialist who will fix this problem.
- The next step is when you start the computer, you need to go into the BIOS system, which can be done by pressing the F 2 combination. The Integrated Peripherals menu, which opens, contains hardware parameters and data.
 Most often, in the BIOS, the external drive is displayed as Drive, or Primary Master; in order to see whether it is enabled or not, in most cases the automatic mode is set, but it is possible that the OFF parameter is assigned to it. In this case, it needs to be turned on.
Most often, in the BIOS, the external drive is displayed as Drive, or Primary Master; in order to see whether it is enabled or not, in most cases the automatic mode is set, but it is possible that the OFF parameter is assigned to it. In this case, it needs to be turned on.
If after turning it on, nothing has changed, and the BIOS still does not see the hard drive, then you need to remove the batteries from the system board, wait half an hour, and put everything back in place, then restart the computer.
Often this helps in solving the problem.
- No motherboard drivers. That is, when installing Windows, the drivers were damaged, or they were not there at all.
In order to install the drivers, you need to insert the drive, the second step is to turn off the computer, connect a device with a SATA interface and turn on the computer.
- The connection adapter (cable) does not work.
You need to check the motherboard connectors for cracks, fractures, and other damage. If such violations exist, the cable must be replaced.
- The drive does not spin.
To find out if it is spinning or not, you need to turn off the computer, open the system unit, turn on the computer and listen to the sound, if there is vibration, then everything is in order, if not, then the problem is in the drive.
The reasons why the drive will not spin is a lack of power or insufficient power.
- The hard drive is faulty. In this case, it is necessary, if possible, to return it or exchange it in the store.
Instructions for connecting a hard drive
1. Turn on your device, then immediately press “del”, the BIOS menu will open. Next, go to the “main” window and press “enter”. Options will open where the hard drives will be listed. You need to find the required hard drive, if it is not there, then select the “sata” connector and press auto mode.
After these steps, the hard drive will be available on the computer.
2. If the first action did not help, the sata interface controller is most likely turned off. Select the line “SATA configuration” and in the “controller” tab click “enable”.
3. After these steps, you need to restart the system and update the hardware configuration. After this, the BIOS should detect the presence of a hard drive.
By checking the connection of all elements and devices of the hard drive, motherboard and other components, you can solve the problem that has arisen such as the hard drive is not detected in bios.
However, you should take into account that it is best to choose a hard drive in a specialized store with a certain warranty period.
You should not purchase HDDs on the market or from dubious organizations. It is also necessary to take into account the characteristics, features and properties of the hard drive.
Basically, most problems can be solved using the proposed methods at home and on your own, but this does not always help to prevent complete breakdown, it's better to consult a specialist.
Sometimes the BIOS does not recognize the connected hard drive. There are many reasons for the occurrence of detailed malfunctions; they can be divided into software and physical ones.
Physical problems
This category includes all malfunctions of the disk or elements responsible for its operation. Since in this case the BIOS will not see the hard drive, you should check them first. In most cases, these problems are eliminated by checking on another computer. If the disk is identified there, then you can move on to the next step.
Cable problem
Often, due to cable damage, data from the disk is not transferred or the disk does not receive commands to operate. In this case, it will not be visible in the BIOS or will be detected incorrectly. Often faulty cable causes displaying “bad sectors” in testing programs.
No matter what kind of damage the cable received (frayed or the solder came off), the solution is always the same - this element needs to be replaced.
Malnutrition
If the hard drive does not start at all, then the reason may be power failure. In rare cases, the power controller on the HDD itself burns out. Much more common is the phenomenon of “power supply drawdown”. To operate the hard drive you need:
- 12 V – for 3.5’;
- 5 V – for 2.5’.
Note: The method described below carries a risk of electric shock! Take the necessary safety measures or consult a specialist.
It is enough to measure the voltage with the power supply unit (PSU) running. If the voltage between the first and fourth contacts does not meet the “+/-10% requirement”, the power supply is faulty. The problem is solved or replacing elements in the power supply (for people who have an idea how to do this), or (which is better) by replacing the power supply itself. 
A special case. Sometimes the hard drive turns off and briefly disappears in the BIOS. When the process of wear of elements begins in the “hot part” of the power supply unit, under prolonged load the voltage may “sag” (drops to values that are not sufficient). This is a rare and annoying problem that is difficult to diagnose.
Jumpers
Old HDDs, also called IDEs, have such a specific thing as jumpers. The position of these miniature elements determines in what mode the disk will operate. The image below shows 2 main states of the hard drive:

It is worth noting that Master and Slave are a conditional division. In fact, it doesn't matter what will be stored on the disk, as long as the jumpers are set correctly.
Similar states on the hard drive itself are dictated by jumpers. If you put them in a position Slave, then the cable connectors will not play a role. Such a HDD will not even be detected on the computer. 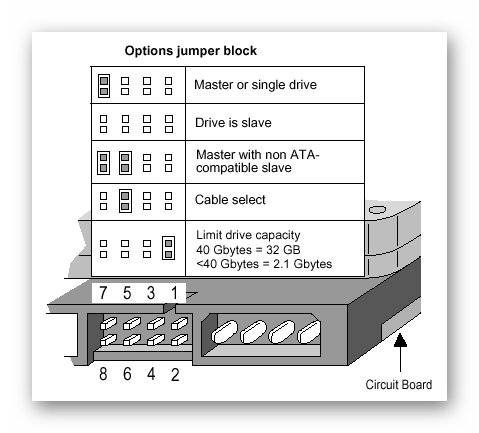
Similar elements are also found in older Sata drives. Modern versions have abandoned the jumpers.
Connecting a second drive
Sometimes adding a second drive presents challenges. Instead of a normal startup and operation, the user is faced with the fact that the motherboard does not see the hard drive. The reasons may be similar to those described above or come from other factors.
Jumper Position and location on the cable. If both drives are IDE, then you should place the jumpers on them in the correct way - so that one hard drive takes on the role of “Master”, and the second “Slave”. Usually this is not enough.
For Sata + IDE combinations you need to configure the second one correctly. Sata itself will be detected without problems.
If the problem occurs with two SATA drives, then you should check their operation separately, and then check the voltage on the power supply.
Physical damage
Chip on HDD may be small and insignificant. If it is a chip on the corner of an iron body, problems may not arise. And if part of the board is chipped, then the hard drive most likely will not work and will not be detected in the BIOS. Such damage can be diagnosed visually, but it is difficult to repair and usually requires purchasing a new drive.
If the BIOS and programs do not see a SATA or IDE hard drive after repair at a service center or from “traditional craftsmen,” it is worth checking the physical presence of the drive. Sometimes, after repairs, specialists simply forget to put all the components of a computer or laptop back in place.
Software problems
Software faults are divided into two main categories, on which the solution depends: BIOS problems and configuration errors. There are not many of them, but one incorrectly installed option can serve as a decisive factor.
SATA/IDE operating mode
In the BIOS configuration there is an item such as “ HDD operating mode" It has 2 or 3 positions: SATA – IDE – Auto. The latter simply adjusts the configuration to the installed drive. The first 2 build a configuration according to a template for a specific drive. 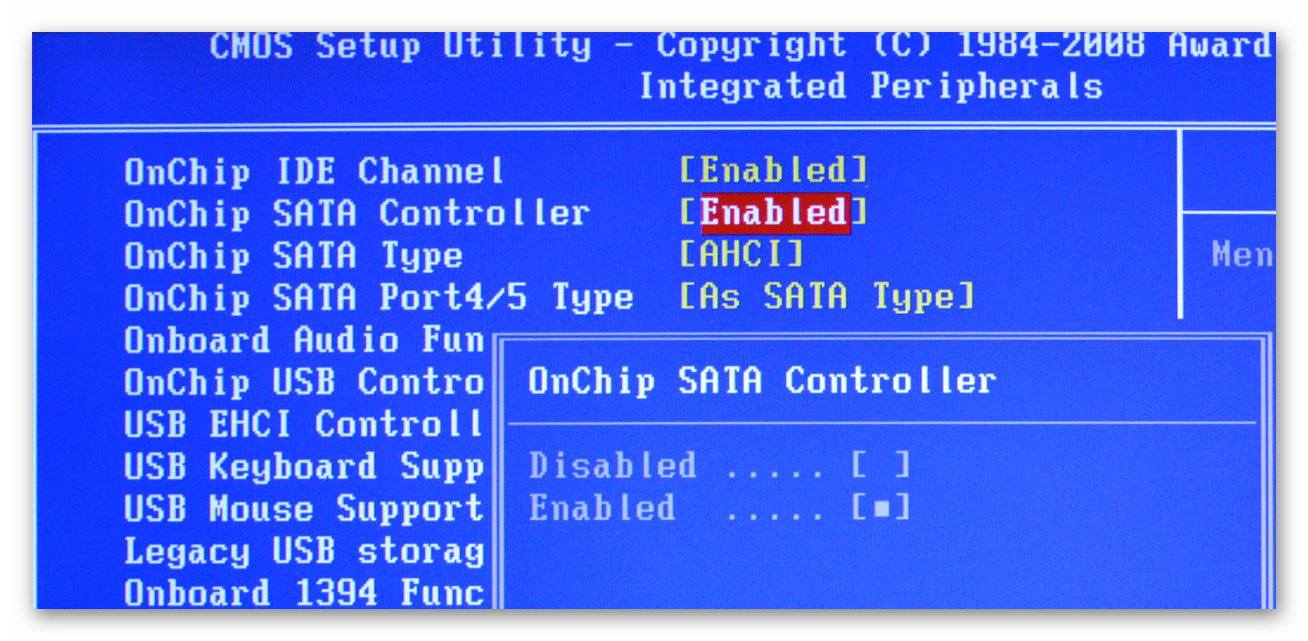
There is a second option: enabling or disabling SATA controllers. Since all this relates to one problem, they are combined into a common point. You should always set the settings in accordance with which HDD is installed in the computer. Otherwise, it will not be detected by the BIOS itself.
Hard drive disabled
Malfunction arising from the above point. In addition to the controller switch, you can mistakenly turn off the disk itself, in this case even boot device priority will not see the hard drive. In this case, it is no longer detected, but can be turned back on when rebooting. 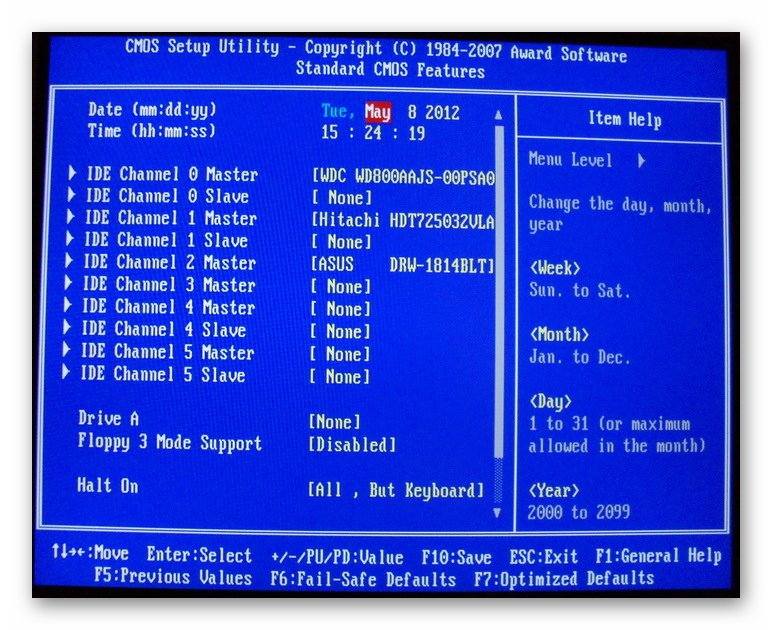
You just need to check the binding of the drives to the corresponding ports (channels. Usually the option is available on the main page of the BIOS).
Bios sees the disk, but Windows does not
This is not a rare case and is usually related to the configuration during installation. In the disk panel in the BIOS there is an option such as “ Sata type" She has 2 options: IDE and AHCI.
Switching the BIOS mode to AHCI if the system was installed in IDE mode will completely block Windows access to the disk. Moreover, Windows itself will stop loading. 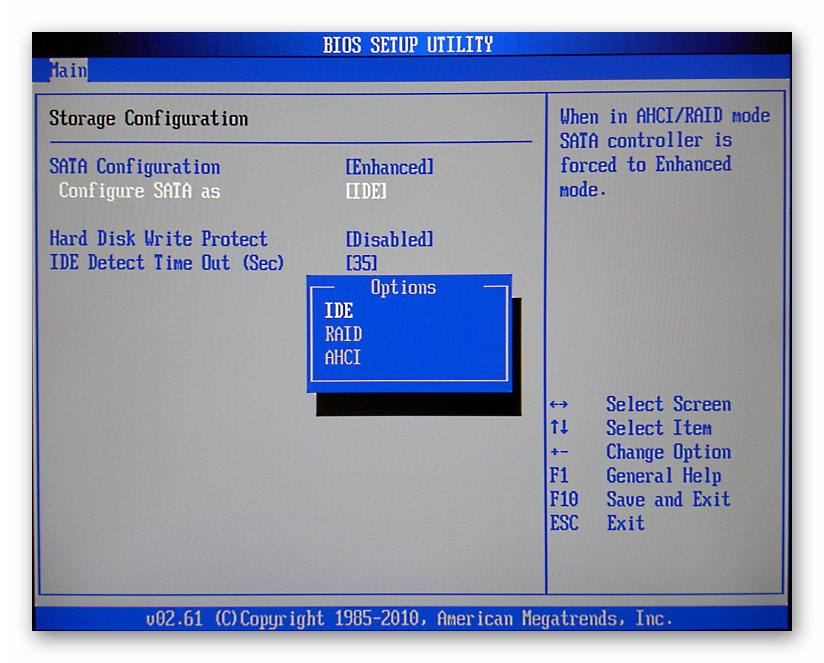
There is another option - the disk is not partitioned. In this case, “Explorer” does not see it. It is present in the list of disk devices and requires marking. Once the process is complete, you can access new local storage.
BIOS does not see IDE HDD
Refers to a situation where:
- BIOS does not have legacy support hard drives;
- Incorrectly installed jumpers (jumpers) or incorrectly configured firmware;
- Lifespan HDD has expired.
Alas, the problem can only be solved with jumpers; in other cases it is easier to find a new IDE drive.
Reset BIOS
Rather than a problem, but a solution. If the battery that supports saving the BIOS configuration state is discharged, then every time the power is turned off settings will be reset. The settings of the disk drives are also reset. They must be entered manually each time.
This can be both a problem and a solution. Resetting the firmware by removing the battery (or installing a jumper. For detailed information, see the instructions for the motherboard) can eliminate a number of the above problems.







