How to make a backup of an Android device before flashing the firmware. How to backup applications without root access on your device
When it comes to creating a data backup or restoration quickly and reliably, many Android users wonder what and how, in this article you will find many ways how and how to backup and later restore!
Why backup?
1. Your personal Android may store a lot of information that is very valuable, which you cannot afford to lose, or for example, you are planning to move from one Android device to another! Of course, when it comes to Google services, for example, everything is very simple here, enter your username and password, wait 2 minutes for it to complete synchronization with Google server and the data is all there, but with other applications you will have to suffer to quickly make a backup copy and restore.
Method No. 1 - backup on Android and restore using standard ADB tools
Thanks to Google, which took care of creating a backup copy, the method is not ideal but still better than none!
So what do you need for this?
- Turn on USB debugging on Adnroid;
- Download the site's proprietary program ADB RUN(from version 3.21.35 and later);
- If not installed driver for PC, install;
- USB cable.
Instructions on how to do it
backup and restore using Adb Run
Creating a Backup
1. Run Adb Run and select the Backup menu
2. Select the first item adb backup

3. Take your Android smartphone or tablet and click the create backup button (you don’t have to create a password)

Restoring from a backup
1. To restore, select adb restore

2. Take your Android smartphone or tablet and click the Recover Data button

Method number 2 - using custom Recovery (root)
First of all, you must have custom Recovery installed! How to do this and how, you can find out in detail from the article download and install Recovery. Creating a backup is not really a backup - it is creating an image of the current firmware state
!
After installed Recovery log into it.
Select the Backup and Restore menu

Select the Backup menu item to create a backup copy

Select the Restore menu item to restore

Method number 4 - DataSync (root)
DataSync is suitable for those who need to back up application data, as well as instant movement them on other device. If you need to create backup copies of applications themselves, and not just their data and settings, then this application is not for you. Learn more about how this application works. DataSync.
Method No. 5 - OBackup (root)
OBackup - Creates backups just like Online Nandroid Backup, only this time the application has an intuitive graphical interface, and you can also send the backup to a cloud drive. Details OBackup.
Method No. 6 - Titanum Backup (root)
Method No. 7 - Helium (root/ root)
A very interesting tool for creating backups. The principle of operation of this application is similar to the operation of the ADB debugging tools; more precisely, it is based on this method, only with the ability to choose which application to create a backup copy for. This application does not work on Motorola
The Helium application can work without Root rights, but if you have them it’s even better (if you don’t have root rights, you need Android to your computer).
How to create a backup using Helium?
1. First, download the application from the official Google Play app store
 free version
free version If you don't have Root rights, then you will also have to download and install the add-on on your PC
You may also need to install drivers on your PC ( for non-Root devices), which are presented on the PC add-on download page

Creating a r.k. in Helium on Root devices
Launch the application refuse from the offer to log into Google Disk, so this function does not work quite honestly (backup, but restoration only works in the paid version of the application)

You can save backups to internal or external memory

To create a backup, select applications in the section RESERVATION, which you want to back up and click the button to start the process


The recovery process is also simple

Creating a r.k. in Helium on NON-Root devices
The process is very similar, only with certain caveats. After downloading and installing the add-on on your PC, run it

Backup or backup allows you to make a copy of all data from the device’s hard drive, which can be restored if damaged. Backup is most often done for computers, but today we will look at options on how to make a full backup of the system firmware on Android.
You can create a backup copy for an Android device in several ways: using a computer, using special applications, using services built into the device.
Recovery is a special program, different from regular applications for the Android system, that creates backup copies and then allows you to roll back to them. Stock recovery is installed on devices initially when they are purchased. This type of backup is performed only if you have root rights to the device.
You can install custom recovery yourself. The latter allow you to perform more different actions, and therefore are popular. The most common of them are: TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project) and CWM (ClockworkMod). Next, you will see how to install backup on Android through recovery.
CWM
ClockworkMod is an older program that has less functionality compared to TWRP. You can replace the stock recovery with it (if it is not already installed as the main one) using the ROM Manager utility in the “Setup recovery” section. One of the features of CWM is the control of only “hard” buttons, i.e., volume control and power buttons, which all Android phones and tablets have.
Algorithm for creating a backup using CWM:
- The phone charge should be at least 60%, and preferably 100%.
- Free up 500 MB or more of free space.
- Turn off, wait about a minute.
- Press and hold the power button and “-” or “+”, depending on the phone model.
- When the upside-down Android icon appears, briefly press the power button and the opposite volume control button to go to the menu.
- In the menu that appears, use the “-” or “+” buttons to select the “backup and restore” section, and confirm the selection with the power button
- In the next menu, select and click “Backup” in the same way
- All! Within 10–15 minutes, a backup of the firmware and all files will be created on your phone.

How to make a backup on Android without applications? Use the same algorithm, since often installed recoveries have similar menus, as well as control methods. In this case, you do not have to get root access.
If this option seems too inconvenient or you need a backup copy of only part of the data, then further you will read how to make an Android backup using TWRP recovery.
TWRP
TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project) is a more advanced utility for the Android system that allows you to use the touchpad and has an almost complete set of functions for working with file storage, software and the operating system. For example, you can back up only selected files. TWRP has a more convenient menu compared to CWM.
To install TWRP, you will need one of the special applications, such as GooManager. In the program menu you need to select “Install OpenRecovery Script”. Then, using the same program, click “Reboot Recovery” and get to the TWRP menu.
IMPORTANT. It is worth noting that the Android device must also have a high battery level and free storage space.
Click “Backup” and select the required partitions. We swipe across the part of the screen highlighted at the bottom, and the program begins creating a copy for the Android system. After a few minutes, click “Reboot system”. The copy is ready.

Using a PC
Obtaining root access, and at the same time mastering various applications, can be difficult for the user, while making a backup of Android firmware on a computer will be much easier for someone than with TWRP. Moreover, you don’t have to download any additional applications for the device.
All you need for this:
- Enabled USB debugging on the Android device (you can do this from the settings).
- Install ADB RUN for your computer, download it for free.
- PC drivers, which are often installed automatically, and a USB cable.
Algorithm of actions:
- We connect the phone to the computer and launch the ADB program.
- Select Backup in the window that opens.
- Next, select the first item in the new menu.
- On your Android device, click “Back up data.” You are also prompted to create a password, but this action is optional.
A copy has been created for you to use if necessary!
Here we discussed the main ways to create a full backup for Android, that is, a firmware backup. In addition, there are various functions and utilities that allow you to make copies of applications or various Android games, contacts, SMS, etc. separately.
Many users of Android devices know that experiments with firmware, installation of various add-ons and fixes quite often lead to the device not working, which can only be corrected by installing the system completely, and this process involves completely clearing the memory of all information. If the user has taken care in advance to create a backup copy of important data, or, even better, a full system backup, restoring the device to the “as it was before...” state will take a matter of minutes.
There are many ways to make a backup copy of certain user information or a complete system backup. What is the difference between these concepts and for which devices it is advisable to use one or another method will be discussed below.
A backup copy of personal information means saving data and content generated by the user during the operation of the Android device. Such information includes a list of installed applications, photographs taken by the device’s camera or received from other users, contacts, notes, music and video files, browser bookmarks, etc.
One of the most reliable, and most importantly simplest ways to save personal data contained in an Android device is to synchronize data from the device’s memory with cloud storage.

Full system backup
The above methods and similar actions allow you to save the most valuable information. But when flashing devices, not only contacts, photos, etc. are often lost, because manipulation of device memory sections involves clearing them of absolutely all data. To reserve the opportunity to return to the previous state of software and data, you only need a full backup of the system, i.e., a copy of all or certain sections of the device’s memory. In other words, a complete clone or cast of the software is created in special files with the ability to restore the device to its previous state later. This will require the user to have certain tools and knowledge, but can guarantee complete safety of absolutely all information.
Where to store the backup? When it comes to long-term storage, the best way is to use cloud storage. When saving information using the methods described below, it is advisable to use a memory card installed in the device. If it is not available, you can save backup files to the internal memory of the device, but in this case it is recommended to immediately copy the backup files to a more reliable location, such as a PC drive, immediately after creation.
Method 1: TWRP Recovery
From the user's point of view, the simplest method of creating a backup is to use a modified recovery environment for this purpose - custom recovery. The most functional among such solutions is.


Method 2: CWM Recovery + Android ROM Manager App
As in the previous method, when creating a backup of the Android firmware, a modified recovery environment will be used, only from a different developer - the ClockworkMod - team. In general, the method is similar to using TWRP and provides no less functional results - i.e. firmware backup files. At the same time, CWM Recovery does not have the capabilities that many users need to manage the process of creating a backup; for example, it is impossible to select individual partitions for creating a backup. But the developers offer their users a good Android application, ROM Manager, using the functions of which you can start creating a backup directly from the operating system.



Method 3: Titanium Backup Android App
Titanium Backup is a very powerful, yet quite easy-to-use tool for creating system backups. Using the tool, you can save all installed applications and their data, as well as user information, including contacts, call logs, sms, mms, WI-FI hotspots and more.

The advantages include the ability to widely customize parameters. For example, you can select applications whose data will be saved. To create a full-fledged Titanium Backup, you must provide root rights, that is, for those devices on which Superuser rights have not been obtained, the method is not applicable.

It is highly advisable to take care in advance of a safe place to store the backups you create. The internal memory of a smartphone cannot be considered as such; it is recommended to use a PC disk, cloud storage, or, as a last resort, a MicroSD card of the device to store backups.
- Install and launch Titanium Backup.
- At the top of the program there is a tab "Backups", let's move on to it.
- After opening the tab "Backups", you need to call the menu "Batch Actions" by clicking on the button with the image of a document with a checkmark located in the upper corner of the application screen. Or press the touch button "Menu" under the device screen and select the appropriate item.
- Next, press the button "START" located next to the option “Make r.k. all user software and system data".A screen opens with a list of applications that will be backed up. Since a full backup of the system is being created, nothing needs to be changed here; you need to confirm your readiness to start the process by clicking on the green checkmark located in the upper right corner of the screen.
- The process of copying applications and data will begin, accompanied by the display of information about the current progress and the name of the software component that is currently being saved. By the way, you can minimize the application and continue using the device as usual, but in order to avoid failures, it is better not to do this and wait until the copy is created; the process happens quite quickly.
- When the process is complete, a tab opens "Backups". You may notice that the icons to the right of the application names have changed. Now these are peculiar emoticons of different colors, and under each name of the software component there is an inscription indicating that a backup copy was created with the date.
- Backup files are stored in the path specified in the program settings.

To avoid loss of information, for example, when formatting memory before installing system software, you should copy the folder with backups to at least a memory card. This action can be done using any file manager for Android. A good solution for performing operations with files stored in the memory of Android devices is.







Additionally
In addition to the usual copying of the backup folder created with Titanium Backup to a safe place, in order to be safe from data loss, you can configure the tool so that copies are created immediately on a MicroSD card.


Method 4: SP FlashTool+MTK DroidTools
Using applications is one of the most functional ways that allows you to create a truly complete backup of all sections of the memory of your Android device. Another advantage of this method is that it is not necessary to have root rights on the device. The method is applicable only for devices built on the Mediatek hardware platform, with the exception of 64-bit processors.
- To create a full copy of the firmware using SP FlashTools and MTK DroidTools, in addition to the applications themselves, you will need installed ADB drivers, drivers for MediaTek boot mode, as well as an application (you can also use, but regular Notepad will not work). Download everything you need and unpack the archives into a separate folder on the C: drive.
- Turn on the mode on the device "USB Debugging" and connect it to the PC. To enable debugging,
first the mode is activated "For developers". For this we follow the path "Settings" — "About the device"- and tap five times on the item "Build number".
Then in the menu that opens "For developers" activate the item using the switch or checkbox "Allow USB Debugging", and when connecting the device to the PC, we confirm permission to carry out operations using ADB.

- Next, you need to launch MTK DroidTools, wait for the device to be detected in the program and press the button "Block Map".
- Previous manipulations are the steps preceding the creation of the scatter file. To do this, in the window that opens, click the button “Create scatter file”.
- The next step is to determine the address that will be needed to indicate to the SP FlashTools program when determining the range of blocks in the memory of the device for reading. Open the scatter file obtained in the previous step in Notepad++ and find the line partition_name: CACHE:, under which there is a line with the parameter linear_start_addr just below. The value of this parameter (highlighted in yellow in the screenshot) must be written down or copied to the clipboard.
- Direct reading of data from the device memory and saving it to a file is carried out using the SP FlashTools program. Launch the application and go to the tab "Readback". The smartphone or tablet must be disconnected from the PC. Press the button "Add".
- In the window that opens, there is only one line. Double-click on it to set the reading range. Select the path where the future memory dump file will be saved. It is better to leave the file name unchanged.
- After determining the save path, a small window will open in the field "Length:" where you need to enter the value of the linear_start_addr parameter obtained in step 5 of this instruction. After entering the address, press the button "OK".

Press the button "Read Back" tab of the same name in SP FlashTools and connect the switched off (!) device to the USB port.
- If the user has taken care of installing the drivers in advance, SP FlashTools will automatically detect the device and begin the reading process, as evidenced by the filling of the blue progress bar.
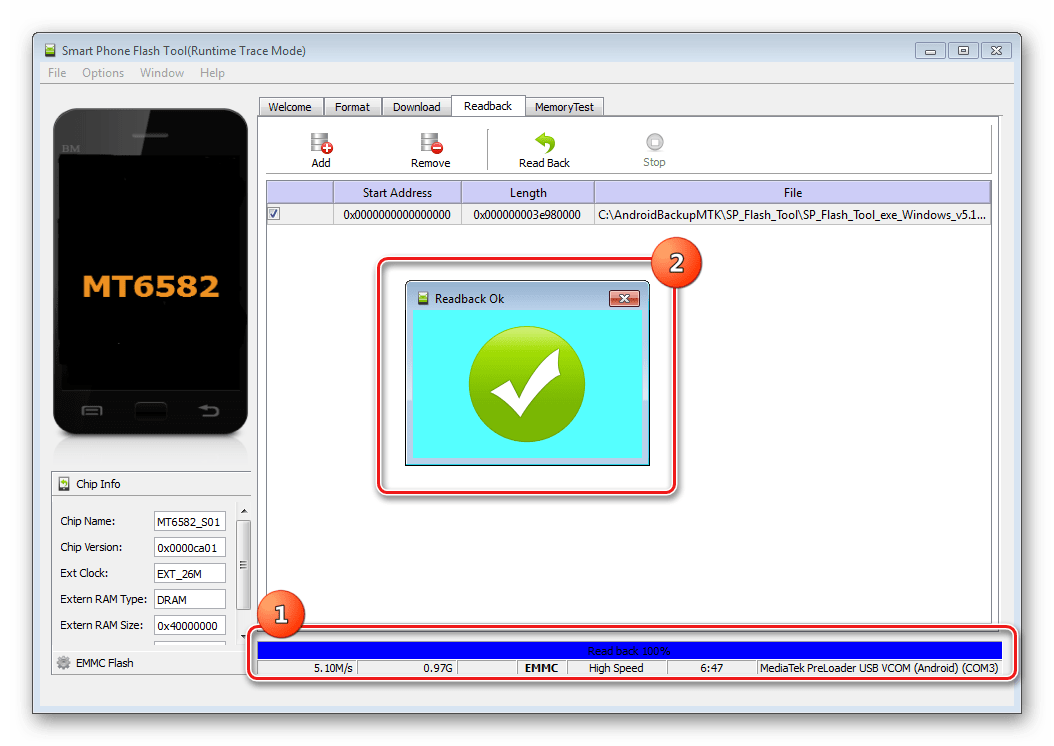
Upon completion of the procedure, a window appears "Readback OK" with a green circle with a confirmation checkmark inside.
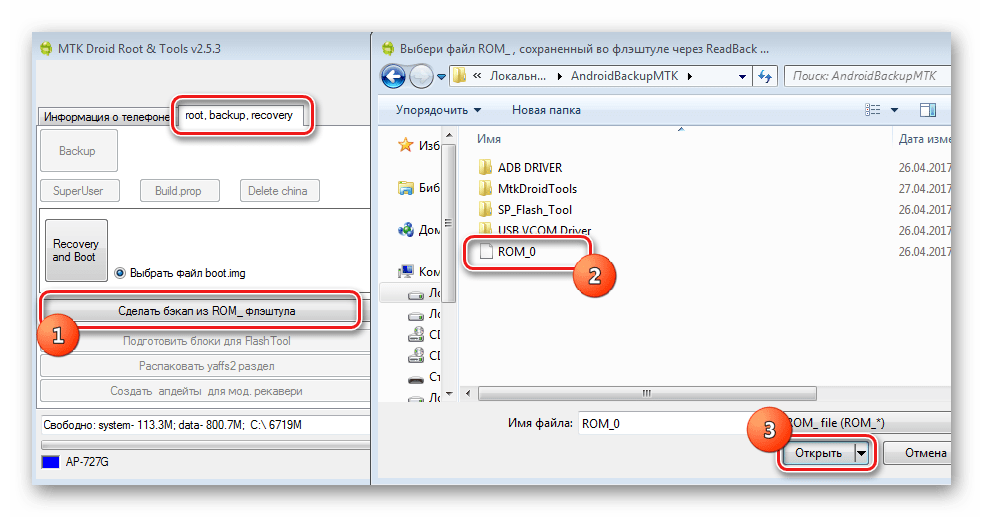
- The result of the previous steps is the file ROM_0, which is a complete dump of the internal flash memory. In order to make it possible to carry out further manipulations with such data, in particular, upload firmware to the device, several more operations are required using MTK DroidTools.
Turn on the device, boot into Android, check that "Debugging via USB" turned on and connect the device to USB. Launch MTK DroidTools and go to the tab "root, backup, recovery". You need a button here “Make a backup from ROM_ flash drive”, press it. Open the file obtained in step 9 ROM_0. - Immediately after pressing the button "Open" The process of dividing the dump file into separate images of partitions and other data necessary for recovery will begin. Process progress data is displayed in the log area.
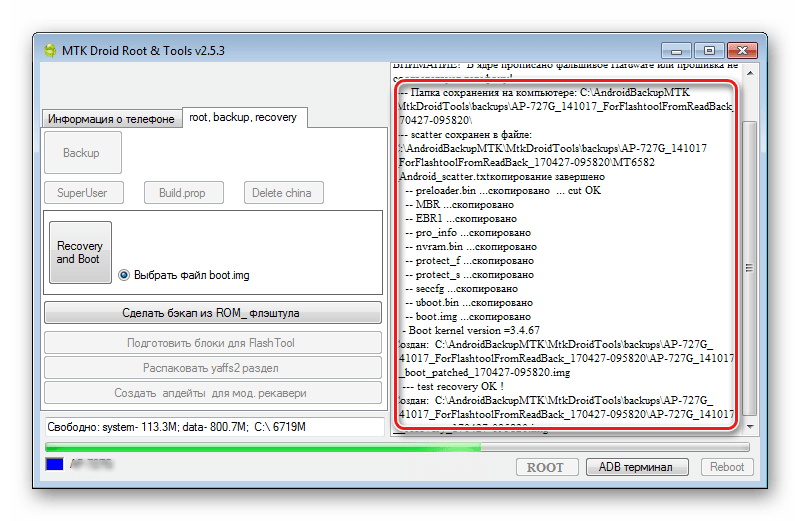
When the procedure for splitting the dump into separate files is completed, the following message will be displayed in the log field: "task completed". This completes the work and you can close the application window.
- The result of the program is a folder with image files of the device’s memory partitions - this is our system backup.



And choose the path to save the scatter.







Method 5: System backup using ADB
If it is impossible to use other methods or for other reasons, to create a complete copy of the memory partitions of almost any Android device, you can use the OS developer tools - the Android SDK component -. In general, ADB provides all the possibilities for carrying out the procedure; only root rights on the device are required.
It should be noted that the method in question is quite labor-intensive and also requires the user to have a fairly high level of knowledge of ADB console commands. To facilitate the process and automate the entry of commands, you can turn to a wonderful shell application, this automates the process of entering commands and saves a lot of time.
- The preparatory procedures consist of obtaining root rights on the device, enabling USB debugging, connecting the device to the USB port, and installing ADB drivers. Next, download, install and launch the ADB Run application. After the above is completed, you can proceed to the procedure for creating backup copies of partitions.
- We launch ADB Run and check that the device is detected by the system in the desired mode. Main menu item 1 - "Device attached?", in the drop-down list we perform similar actions, select item 1 again.

A positive answer to the question whether the device is connected in ADB mode is the ADB Run response to the previous commands in the form of a serial number.
- For further manipulations, you need to have a list of memory partitions, as well as information about which “disks” - /dev/block/ the partitions were mounted. Using ADB Run, getting such a list is quite easy. Go to the section "Memory and Partitions"(item 10 in the main menu of the application).
- In the menu that opens, select item 4 – "Partitions /dev/block/".
- A list opens listing the methods by which attempts will be made to read the necessary data. Let's try each item in order.

If the method does not work, the following message is displayed:

Execution will have to continue until the full list of partitions and /dev/block/ appears:

The received data must be saved in any available way; there is no automatic saving function in ADB Run. The most convenient way to capture the displayed information is to create a screenshot of a window with a list of sections.



About five years ago, smartphones were exclusively owned by people who needed their functionality. Today, thanks to the development of the Android device market, almost everyone has these gadgets. The platform is quite customizable and develops quickly - new major versions are released every year, and throughout the year, manufacturers pamper users with updates to existing OS versions several times. Because of this trend, it is very important to know and be able to make a firmware backup, so that in case of an unsuccessful update or in any other situation, you can quickly rollback to a working system without losing your data and information.
In principle, there are quite a few ways to make a backup, but the most common and convenient is install custom recovery with this function. The most popular alternative recovery options are CWM (ClockworkMod recovery) and TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project). CWM- one of the very first such projects - it is quite minimalistic and is controlled exclusively by “hard buttons” - the volume buttons and the power key. It has only the most necessary functionality (including the backup function). TWRP a more advanced project. It has touch controls and quite a few features, the most useful of which is perhaps the built-in file manager, which will allow you to copy your data from the internal memory to a flash drive if the phone refuses to boot.
Let's take a brief look at each of these two alternative recovery options, consider how to make a backup using them, and show you another way that will allow you to do this directly from a working system. We will also consider options for backing up only certain data (SMS, MMS, etc.) 
CWM

ClockworkMod recovery is a modified unofficial recovery, which is produced for almost any more or less popular phone model. Installation is possible either instead of standard recovery or in parallel with it. With its help, you can install unofficial firmware, create backups, reset user data and format partitions. You can also create separate partitions on a memory card, etc. 
To make a backup of the file system of your Android device you need to go into CWM recovery (this procedure may differ slightly on different phones). Then you need to use the volume buttons to go to backup and restore and select either Backup (full backup of the entire system) or Advanced Backup– this will allow you to select the partitions that you want to save (most often these are data and boot), which will allow you to save time and space on the flash drive.
Video about installing ClockworkMod recovery
TWRP

TeamWin recovery is also a modified unofficial recovery, which is available for most Android device models. It allows you to perform many more actions with the device than standard recovery and than CWM, but is less common than the latter. TWRP will allow its users to:
- install unofficial and official firmware;
- install corrections and additions;
- supports connection in ADB mode;
- create backup copies of both the complete firmware and its individual parts;
- format partitions and create them.

To make a backup using TeamWin recovery, you need to go into it, go to the Backup item and make a snapshot of the system, and you can choose which sections of the system you need to save.
Video about installing eamWin recovery
Restoring from a backup
To begin with, for greater safety, you need to transfer the folder with the saved firmware to your computer’s hard drive, write it to an optical disk, upload it to the cloud, etc. In this case, even if you lose the flash drive, you will always have the opportunity to roll back the system to its old state. Then you will need to go into recovery again and select Restore, and then mark the partitions that you want to restore (in the case of CWM, you will need to go to Advanced restore). After waiting for the operation to complete, reboot the device.
Another way to backup a partition
If you are somehow not satisfied with the previous methods, then there is another one that is much less commonly used, but with its help you will definitely preserve all connections and file rights. To implement it you will need a phone with root rights , on which the terminal emulator is installed.
First, open a terminal emulator and type:
su
After this, a confirmation window for root rights should appear (if you have not already confirmed them before. Then type:
dd if=/dev/block/“block number” of=/sdcard/system.img bs=4096
Where instead of “block number” you should write the number of the section you want to save. To restore the partition, the resulting file will need to be flashed via fastboot, like a regular img image.
Saving SMS, MMS and other content
If you want to “move” to a new system, then you will only need to restore old messages and, possibly, some files. The files will remain on your memory card, so you don’t have to worry about this, but text messages will have to be saved manually. There are many free programs on Google Play; to save them, you just have to choose the most convenient one.
It is also worth noting that Android has well-developed functions for saving application data and restoring applications themselves, therefore, you will not need to worry about this operation - the system will do everything for you.
A full backup of Android prevents the loss of important information for the user in the event of software and hardware failures, a virus attack, as well as when the device fails, that is, it turns into “”. Backup is recommended to be used on all mobile devices, especially since there is nothing complicated about it. Let's look at how to create a backup copy of the Android operating system.
Methods for backing up data for Android
Today, owners of smartphones and tablets are endowed with fairly broad capabilities for saving personal information in the event of various failures and other unforeseen situations. Like Windows, Android also has certain tools for backing up the system, that is, for creating a restore point. Possibly on a smartphone.
Backing up data located on Android can be done using:
- Built-in resuscitation service android backup service;
- Additional software installed on a PC or directly on a smartphone (tablet).
Considering what a backup is, it should be noted that to backup Android along with the firmware on the device, you need to activate root access. If you do not have Superuser rights, you will only be able to save personal data (SMS, contacts, photos, music, etc.), as well as the settings of some applications.
Creating a backup using built-in Android capabilities
All gadgets running Android OS have the ability to connect to Google and enjoy many of the benefits of this service absolutely free (synchronize with a PC, write personal data to a cloud drive, etc.). One of the very useful Google tools is the android backup service. It allows you to create Android backups and backup data from your phone to virtual storage automatically.
Before you make an Android backup using the android backup service, you need to create your Google account and assign your mobile device to it. This is done as follows:
After Google is connected, we make a backup of the system:

To return data to Android via the Android backup service (for example, after a hard reboot), just re-link to your Google account, enter the “Restore and reset” section and start the recovery procedure.
System backup through the Recovery environment
Every mobile device running Android OS is equipped with . However, the standard program has somewhat limited capabilities that do not allow you to make a full backup of the firmware. Therefore, many owners of smartphones and tablets install a custom version of it instead of regular Recovery.
Let's look at how to make an Android backup via:

It may take some time to create a copy of the firmware. When making a backup, it is prohibited to do any actions with the device (for example, install/remove a micro sd card), as this may negatively affect the final result.
When considering the Recovery area, you should also know how to restore the system from a previously created backup. To do this, in the backup and restore section you need to select the restore item. After the smartphone reboots, all your data, along with the firmware, will return to its place.
Creating a backup using additional software
A backup copy of data can also be recorded using special programs installed on a computer or mobile device. There is a lot of similar software on the Internet, but the most effective applications in this area are considered to be:
- TWRP Recovery.
Let's figure out how to backup Android for each of these programs.
This utility backs up the Android system to a computer. Therefore, before starting work, you need to prepare a USB cable to connect your PC to your phone. The sequence of work will be as follows:
- Download and install the application on your computer.
- Enable USB debugging on your smartphone. To do this, you need to go to the “For Developers” section and select the appropriate item.

- Launch MyPhoneExplorer and connect the gadget to the PC.
- Go to the “File” menu and select the switching type, as shown in the image.

- To create an Android backup, open the “Miscellaneous” tab and click “Create”.

- We indicate the location where the copy will be stored.
- We note what needs to be saved and start the backup process.

- If necessary, restore Android using the created backup by selecting the “Restore” function in the “Miscellaneous” window.
TWRP Recovery
This backup program is installed directly on your mobile device. However, before you make a full backup, you need to unlock Superuser rights.







