Types of LCD monitors for computers. Which computer monitor to buy. for computer displays
A computer monitor is a device designed to display visual (graphic, text, video) information.
Also, some monitors have built-in sound speakers and can thus reproduce sound, but this feature is not included in the main characteristics of the monitor.
When purchasing or assembling a personal computer (PC) from separate ones, you should definitely pay attention to the characteristics of the monitor, which we will consider below.
Previously, a monitor was called a display; now this name is rarely used.
1 Diagonal length and proportions of the monitor
 Diagonal is measured in inches. 1 inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters. Previously, the measurement (“standard”) of an inch was the width of the thumb on an adult man’s hand. An inch when indicating the diagonal of a monitor is represented by a quotation mark “ - in the form of a double stroke. In English, inch is inch, abbreviated as in.
Diagonal is measured in inches. 1 inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters. Previously, the measurement (“standard”) of an inch was the width of the thumb on an adult man’s hand. An inch when indicating the diagonal of a monitor is represented by a quotation mark “ - in the form of a double stroke. In English, inch is inch, abbreviated as in.
Most often you can find monitor models with diagonals of 15”, 17”, 19”, as well as 21”, 23” and 27 inches. The last option (27”) is more suitable for professional designers, photo editors, video editors, etc. Of course, ordinary users can also use it if they have the opportunity and desire to have a large monitor.
Monitors may have the same size in inches, but they will differ in proportions (Fig. 1).

Rice. 1 Monitors have the same diagonal, but different proportions
As for the proportions (the ratio of the length and width of the sides of the monitor), three formats are most widespread -
- 16:9,
- 16:10,
These numbers mean the following. 16:9 - this means that the width of the monitor (horizontally) is 16 conventional units, and the height of the monitor (vertical) is 9 of these same conventional units. More precisely, the width of the monitor is greater than its height by 16 divided by 9 times, that is, 1.78 times.
And, for example, a ratio of 4:3 means that the width is greater than the height by only 4 divided by 3 times, that is, 1.33 times.
Monitors with an aspect ratio of 16:9 and 16:10 are widescreen. They are good for watching widescreen and widescreen video movies. It is convenient to open several windows at the same time.
Monitors with an aspect ratio of 4:3 are convenient for those who work with editors, with graphic files, etc., but for others they are more familiar.
Monitors with an aspect ratio of 4:3 are often more convenient for work, and 16:9 for entertainment. Nowadays, widescreen monitors are also used more often for work, simply because they are more common.

Rice. 2 Two monitors in one housing
Widescreen monitors are convenient for those who like to work with several at once. Such users often use PC configurations with 2 (Fig. 2) or even 3 monitors at the same time.
The diagonal length and proportions of the monitor are what users pay attention to first, but the main characteristics of the monitor, of course, do not end there.
2 Type
Currently, there are only two main types of monitors:

CRT monitor
As for CRT, this abbreviation stands for “cathode ray tube”.
These monitors are similar to old TVs (they are almost the same size and weight). They are older and are rarely used due to their large size, energy consumption and harm to the eyes.
Cathode ray tubes use high voltage, fast charged particles, and other technical things that are more harmful to users than more modern LCD displays.
LCD is an abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display, which translates as liquid crystal display.
LCD monitors are more compact and lightweight because they can be almost flat in shape. Therefore, today they are used almost everywhere.

LCD monitor
The picture on LCD monitors is formed from a set of small dots (pixels), each of which can have a specific color. There are no harmful effects on the user and his eyes that cathode ray tubes had.
The first models of LCD monitors were slow, they could not reproduce fast-changing images without distortion, and therefore cathode ray displays were competitive for some time. However, technology does not stand still, and modern LCD monitors no longer have the disadvantages of their predecessors.
Today, when buying a monitor, you can see a varied range of exclusively LCD displays. Cathode ray tubes are becoming a thing of the past.
3 Resolution
This is the number of pixels (the dots that make up the display) vertically and horizontally. The more pixels, the higher quality image can be obtained. And vice versa, the fewer there are, the more blurry, less clear, and lower quality the image will be. Therefore, if you want to see clearer pictures, you need to have more pixels.
In general, a pixel is the smallest point on a monitor screen. The whole picture is made up of such points. The more dots and the fewer these dots, the clearer the image. Hence the need to have more pixels to get better quality images.
Typically, resolution depends on the size of the display and its aspect ratio. For example, you can often find:
- 16:10 format monitors have a resolution of 1440x900,
- for 4:3 format monitors – resolution 1600x1200,
- 16:9 format monitors have a resolution of 1920x1080.
Numbers, for example, 1920x1080 mean:
– horizontally the monitor has 1920 pixels – the minimum points from which the image is composed,
– the monitor has 1080 pixels vertically,
– in total there are: 1920 multiplied by 1080 equals 2,073,600 pixels, that is, more than 2 million tiny dots, from which a beautiful, clear color image is formed.
In addition, the term pixel density is often used. Density is calculated using the formula “the number of points on any side divided by the length of this side.” This is needed to represent how many pixels are in one millimeter or one centimeter of the screen. But, as a rule, people have already gotten used to pixels, so the phrase “pixel density” is used much less often.
4 Matrix type
There are many types of matrices, they are not so easy to understand. They depend on the manufacturing technology of the matrix, and due to this they differ from each other in image quality, viewing angle, speed of image change and other parameters.
The viewing angle means that in some places the image is visible from all sides, and in others strictly at almost a right angle, so that the “neighbor” cannot see what is shown on your monitor.
The following types of matrices are distinguished:
– relatively inexpensive, but not the highest image quality TN+film panels. Their disadvantage is small viewing angles (move a little to the side and you won’t see anything), a decrease in brightness and contrast if you look at the image from the side and not at a right angle, etc.
– numerous IPS matrices with different nuances and differences from each other, having wide viewing angles, deep blacks, and good color rendition. Various types of such matrices can have both short (bad, slow) and fast (good, high-speed) response times, which allows slow matrices to be used for office work, and fast ones for watching videos, games and other applications that require fast graphics .
– VA matrices, PVA matrices and other types of matrices that differ from each other in response time (speed), color rendering, viewing angles and other characteristics.
5 Contrast level and viewing angle

Contrast is measured by comparing the brightness of the monitor's white and black pixels. The average value of this indicator is 1:700. The numbers mean that the brightness of black pixels is 700 times less than the brightness of white pixels, which is a very decent value. Although now it is quite common to find monitors with a contrast ratio of up to 1:1000.
The viewing angle affects from what position in relation to the monitor you can easily distinguish the picture. Many modern monitors have a viewing angle of 170-175 degrees.
We remember from school geometry that 180 degrees is a rotated angle, that is, looking at the monitor tangentially to its plane. Therefore, a viewing angle of 175 degrees is an opportunity to see the image even when standing to the side of the monitor. In other words, the picture is visible even if you direct your gaze almost parallel to the display.
6 Pixel response time
Also quite a significant indicator. The shorter the response time, the faster the picture will change (pixels will respond faster to the signal).
High-quality modern monitors have a response time of 2-9 milliseconds. The number 9 milliseconds means that the image of each pixel can change more than 100 times per second.
And the number 2 milliseconds means the ability to change the image of each pixel 500 times in 1 second! We remember that the human eye no longer has time to distinguish between changes in a picture with a frequency of more than 24 times per second, and therefore 500 times per second is a very good result!
The faster the response, the better quality moving pictures the monitor can reproduce. Therefore, fans of computer games and those who like to watch high-quality films on a monitor screen prefer monitors with high response times, and are willing to pay extra money for this quality.
7 Connectors and ports for connecting a monitor
An important point when choosing a monitor is the option of connecting it to a computer. First of all, you need to know what connectors are on the computer.
If the monitor is selected for a desktop PC, then the computer may have different ports, for example DVI, VGA, HDMI.

Laptops usually use a VGA port to connect an external monitor.

But Apple computers use ports such as Mini DisplayPort and TunderBolt. All this should be kept in mind when choosing a monitor.
As a rule, monitors have the ability to connect to a DVI and (or) VGA port, but this must also be clarified.
If you need to connect the monitor to other ports, you may need special adapters with which the monitor can be connected to the computer. And then you need to take care of these adapters in advance.
Survey
.Already more 3,000 subscribers.
A monitor is an integral part of any computer; it is necessary for the exchange of information from the computer to the user. The monitor is a universal device for visually displaying graphic and text information.
Monitors vary in display size, video adapter type, and screen type. Based on the type of screen, a computer monitor can be:
- Plasma.
- Electron beam.
- Liquid crystal.
Cathode ray monitors are voluminous, large in size, and have an appearance reminiscent of older model color TVs. They work on the same principle as old TVs.
Such monitors are called CRTs, and they are still produced today. Information on the screen of such monitors appears thanks to a cathode ray tube. The electron gun is located in the neck of the device, it heats up and releases a stream of electrons. Deflection and focusing coils direct the flow to the desired point on the phosphor-coated screen. Under the influence of electron energy, luminous phosphor dots create an image.
LCD monitors are the most common type today. The display is based on the properties of liquid crystals. The light filter located in the display creates light waves, and the polarizing filter located opposite, rotating, changes the amount of incoming light energy. Thus, the screen brightness is adjusted. In order to transmit colors, the display has a third light filter, which has three cells (blue, red and green) for each pixel of the image.
Today, LCD monitors are leaders in the computer market, as they have a huge number of advantages. These monitors are compact in size, flicker-free, provide very high quality images and do not emit electromagnetic waves.
Such a monitor can be conveniently placed on the desktop surface and you can get great pleasure from watching movies with high image clarity without having a negative impact on your own vision.
Plasma monitors have many advantages, but at the same time, they also have a fairly high price. Phosphors, which are located on the surface of the screen, glow under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Ultraviolet radiation creates a light discharge in a rarefied gas environment, and a conductive cord consisting of ionized molecules (plasma) appears between the electrodes.
The brightness of an individual element depends on the glow time of the cell. Images on plasma monitors do not flicker, which provides eye protection.
Almost any catalog of computer equipment contains the above types of monitors.
If you are reading these lines, then you know exactly what a monitor is. Otherwise, where would you read these lines from? From the monitor we receive all text and graphic information. Without it, the computer is just a box in which there is a lot of things, but it is impossible to know what exactly.
What types of monitors are there?
From the time of their birth to today, monitors have undergone a certain “evolutionary” development. It resulted in the birth of three types of devices.
1. CRT monitors.
They are distinguished by their large overall dimensions, impressive weight and flickering screen.
A mandatory design element of these devices is a cathode ray tube (CRT). It is a glass vessel filled with vacuum. On one side the tube is narrow, like a neck, and on the other it is wide and flat. This is the screen. On the front side it is coated with a special substance – phosphor. It has the property of glowing under the influence of a flow of electrons. The slightly flickering image on a CRT monitor screen is the result of bombardment of the phosphor by a controlled flow of charged particles.
In color monitors, the screen is covered with tiny particles of red, blue and green phosphors. The flow of charged particles is provided by three electron guns. This is how a color image appears on CRT monitor screens.
CRT monitors are becoming a thing of the past due to their main disadvantages - large dimensions, high power consumption and electromagnetic radiation. But at the same time, they have advantages that more modern types of monitors cannot always boast of. The main ones are the high speed of displaying images on the screen and its high quality from any viewing angle. Therefore, DVD movie lovers and avid gamers are in no hurry to part with CRT monitors.
2. Liquid crystal monitors.
They are also called LSD monitors, which are basically the same thing. The image reproduction technology in such devices is based on the use of liquid crystals with unique properties. Depending on the direction of the electromagnetic field, they are capable of transmitting or not transmitting a certain color component. That is, we can say that liquid crystal molecules are filters that can be controlled and thereby regulate the output of the desired color effects on the screen in the form of images.
The main advantages of LSD monitors include their compactness, low power consumption, and the absence of radiation and screen flickering. That's why most people today probably want buy a monitor with LCD screen.
3. Plasma monitors.
They are distinguished by expressive brightness and contrast of the image. But there are also disadvantages - relatively high power consumption and low resolution. The screen of a plasma monitor consists of many small flasks filled with an inert gas. Their inner surface is covered with a phosphor, the smallest dots of which are illuminated with the desired color under the influence of a plasma discharge in an inert gas environment. The discharge occurs as a result of applying voltage to the electrodes with which the flasks are “stitched”.
Having considered all types of monitors, we can come to the following conclusion that liquid crystal devices are currently the most in demand. Thanks to their undeniable advantages, they were able to completely displace CRT monitors from the market. Plasma designs for working with a computer are rarely used. They are more often used as televisions and monitors for large audiences.
If the information about monitors in this article is not enough for someone, then you can find out more about these devices .
Monitor
One of the important components of a personal computer is its video system, which includes the following elements:
· monitor;
· video adapter board;
· a set of driver programs.
All modern monitors can be divided into two classes:
· cathode ray tube monitors(CRT);
· LCD monitors(LCD monitors).
In turn, among each class there are colored And monochrome monitors.
To form the color of a point on a monitor screen, three primary colors are usually used: red (Red), green (Green), blue (Blue) and an intensity or brightness signal (Intensity), i.e. so-called palette IRGB. All other colors are obtained by mixing the three primary colors.
Depending on the type of signal that controls the electron beam, CRT monitors are divided into analog And digital.
The operating principle of liquid crystal monitors is that when voltage is applied to the liquid crystal, it changes its color.
The advantage of an LCD monitor is that there are no harmful emissions during its operation. The disadvantage lies primarily in its high cost and low performance.
LCD monitors include:
backlit monitors;
· monitors without backlight;
Non-backlit monitors can only operate in sufficient ambient light. However, their clarity is lower than that of backlit monitors. However, backlit monitors are more expensive and their internal batteries drain very quickly.
LCD monitors are divided into:
· active matrix monitors;
· passive matrix monitors.
The contrast of monitors with an active matrix is much higher than that of monitors with a passive matrix, so for the human eye it is more optimal to work with a monitor on an active matrix, but their cost is much higher.
A computer monitor can operate in two modes: text and graphic. IN text mode The display screen is divided into 25 lines of 80 characters per line. This mode is used to display predefined characters. These symbols include large and small Latin letters, letters of the Russian alphabet, numbers and other various symbols.
IN graphic mode The image is displayed on the display screen by dots (pixels). In this mode, you can draw pictures, create tables, build graphs, etc. Of course, in this mode you can also display text information, but the performance will then be lower than when working in text mode.
A distinctive characteristic of graphics mode is that this mode requires significantly more video memory than character mode.
Main characteristics of monitors
Resolution monitor is determined by the number of pixels that are reproduced horizontally and vertically on the screen, for example, 800x600 pixels. The higher the resolution, the clearer the image on the screen, however, the image itself becomes smaller.
The next characteristic is Screen size diagonally. There are several standard monitor screen sizes, measured in inches: 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 21. The optimal monitor size for the human eye is 15 - 17 inches. However, it should be noted that with an increase in screen size by one type, the cost of the monitor increases by 20-30%.
Frame frequency measured in Hertz and determines how many times in one second the screen image is updated. The human eye perceives changing images with a frequency of 25 Hz as continuous movement. However, the higher the frame rate, the more stable the image and the less tired the human eye is. The recommended frame rate should be at least 75 Hz.
The clarity of the image on the screen, in addition to resolution, also depends on screen grain , i.e. on the size of the phosphor dots. The smaller the phosphor dots, the higher the image clarity.
Usually they talk not about the sizes of the points themselves, but about distance between them. This parameter can be in the range of 0.41 - 0.22 mm. However, for good models the range is 0.28 - 0.22 mm.
The operation of a CRT monitor is accompanied by various radiations, such as x-rays, infrared radiation, radio radiation, and electrostatic fields are also created around the monitor. Therefore, on older monitor models it is necessary to use special protective screens (filters).
Currently, mainly monitors with low radiation levels are produced - the so-called monitors Low Radiation. These monitors comply with the MPRII specification developed by the Swedish National Measurement and Testing Council. However, since 1991, the Swedish Confederation of Professional Workers has introduced even more stringent standards: TSO91, TSO92, TSO95, TSO99 and etc.
All modern monitors, as a rule, meet the energy saving standard Energy Star(these are usually called “green” monitors). According to this standard, the monitor must consume no more than 30 watts on average, use no toxic materials, and be 100 percent recyclable at the end of its service life.
In accordance with the Energy Star standard, there are 4 power consumption modes for the monitor:
· On (operating mode with maximum load);
· Standby (standby mode);
· Suspend (suspension of work);
· Off.
In On mode, the computer works actively and consumes maximum energy. In Standby mode, the video signal is turned off and contrast and brightness are kept at a minimum level. Pressing any key or moving the mouse returns the monitor to its working state. Power consumption in Standby mode is reduced by 20%. In Suspend mode, the high voltage in the monitor is turned off (i.e., the CRT is turned off). The monitor can return to operating mode only after a few seconds. Energy consumption in Suspend mode is reduced by approximately 70%. And the last mode, Off, provides maximum energy conservation (up to 95%). In this mode, almost all blocks in the monitor are disabled.
Video adapter
The video adapter is used to convert the digital signal processed by the computer into a video signal sent to the monitor.
Currently there are the following types of video adapters:
1. VGA(Video Graphics Array) - provides a resolution of 640x480 pixels and displays at least 16 colors (4-bit palette, i.e. 2 4 =16 ).
2. SVGA(Super VGA) - provides resolution 800x600 pixels and displays at least 256 colors.
3. VESA- have become widespread recently and are characterized by more stringent requirements for the video system. Provides a minimum resolution of 1280x1024 pixels and displays 16.7 million colors (24-bit palette).
Currently, the main video modes in which monitors and, accordingly, video adapters operate are High Color And True Color. In High Color mode, the video adapter displays 32,000 colors; in True Color mode, the video adapter displays 16.7 million colors.
Modern video adapters usually have graphic accelerator , which increases the performance of the video system by reducing the amount of information transmitted over the computer system bus, i.e. it relieves her significantly. Part of the image can be created by these devices without loading the main processor.
Practical task
1. Determine the model of your personal computer monitor and write it down in the report (for the sequence of answers, see 4. Creating a report).
2. Swipe monitor classification your personal computer, write it down in the report.
3. Indicate whether your monitor supports the standard Energy Star.
4. Indicate which safety standard your personal computer monitor meets.
5. Determine and record the diagonal screen size of your monitor.
6. Turn on and boot your personal computer.
7. Open the folder My computer and then the folder Control Panel.
8. Using folders System And Screen, determine and report the current resolution of your monitor.
9. Using a monitor testing program, determine and report the maximum possible resolution of your monitor.
10. Determine and record your monitor's current color palette.
11. Determine and record the maximum possible color palette of your monitor.
12. Determine and report your monitor's frame rate.
13. Determine and report the maximum possible frame rate of your monitor.
14. Determine and record the model of your video adapter.
15. Determine and report the amount of video memory used by the video adapter.
16. Determine and report which resources the video adapter is using.
17. Determine and record in the report which driver is used by the video adapter.
Create a report
After completing the practical task, the student must draw up a report, which must reflect the following provisions:
· number and name of laboratory work;
· purpose and plan of the lesson;
· answers to the questions stated in the practical task:
1) Monitor model.
2) Monitor classification.
3) Standard support Energy Star.
4) Monitor safety standard.
5) Monitor screen size.
6) Current monitor resolution.
7) The maximum possible monitor resolution.
8) Monitor color palette.
9) Monitor frame rate.
10) The maximum possible frame rate of the monitor.
11) Video adapter model.
12) The amount of video memory used.
13) Video adapter resources.
14) Video adapter driver.
Reply in writing to the following questions:
1. How many operating modes does the monitor have?
2. What types of video adapters do you know?
3. What main characteristics of monitors do you know?
4. How many colors does the palette use? IRGB to create a color image?
5. What does Energy Star mean?
6. What safety standards do you know?
7. How many colors (exact number) can 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit color palettes produce?
After completing the report, the student submits it to the teacher and defends it. After successfully defending the report, the student moves on to the next laboratory work. It is not allowed to perform and report the following laboratory work without successfully defending the previous work.
Main literature
1. Filippov M.V. Computers, computer networks and telecommunication systems: Textbook. – Volgograd: Publishing House VF MUPC, 2002. – 172 p.
2. Filippov M.V. Computer science. Short course: Textbook. – Volgograd: Publishing House VF MUPC, 2001. – 172 p.
3. Computer Science: Textbook / Ed. N.V. Makarova. –M.: Finance and Statistics, 1997.-768p.
4. E.A. Jakubaitis. Information networks and systems. Reference book. –M.: Finance and Statistics, 1996.
5. Computer technologies for information processing / Ed. S. V. Nazarova. –M.: Finance and Statistics, 1997.
additional literature
6. Kolesnik A.P. Computer systems in financial management. –M.: Finance and Statistics, 1994.
7. Information systems in economics: Textbook / Ed. V.V. Dick. - M: Finance and Statistics. – 272s.
8. Economic informatics and computer technology / Ed. V.V. Evdokimova. – St. Petersburg: Peter Publishing, 1997.
9. Economic informatics and computer technology. Textbook for students of economic specialties of universities / ed. V.P.Kosareva, A.Yu. Koroleva - M., Finance and Statistics, 1996
10. B.M. Kagan. Electronic computers and systems. - M.: Energoatomizdat, 1985.
11. B. Nans. Computer networks. –M.: BINOM, 1996.
12. A.A. Gorchakov, I.V. Orlova. Computer economic and mathematical models: Proc. manual for universities. - M.: Computer, UNITI, 1995. - 136 p.
Related information.
User question...
Good afternoon. Please help, I want to buy a monitor exactly the same as the one I have now, but I don’t know its exact model. All that is there is a sticker on the body of the device, which only indicates its brand (Samsung). How can I find out the model of my monitor without disassembling it and taking it to a specialist shop (and is this possible)?
Hello.
There are several ways to determine your monitor model and they are all quite simple. And, by the way, I should note that the monitor model is sometimes needed not only in cases when you want to replace it, but also in order to know its capabilities and acceptable operating modes.
Let's look at a few ways below...
Determining your monitor model
Method number 1: sticker on the body
The easiest and fastest way to determine what kind of monitor you have is to find the sticker on the device case. If there is no sticker or inscription on the front side, then in most cases there is one on the back of the device, next to the VGA (D-Sub), HDMI, etc. inputs.
The example below is shown in the photo: monitor model AOC F22s+. Actually, knowing the model of the monitor, you can easily find out all its characteristics on the Internet (on the same Yandex market)...

Method number 2: using special. utilities (Aida, Everest, Astra 32)
Sometimes, there are no stickers on the monitor body (for example, the device could simply come off due to years of use...).
In this case, I recommend using one of the utilities to determine the characteristics of your computer. There are quite a lot of them now, but not everyone can get the maximum information about your monitor. I recommend using Everest or Aida 64 (link to them below).
Determining computer characteristics -
In a programme EVEREST just open the tab "Display/Monitor" , then you will see the following information: monitor name, ID, model, monitor type, serial number, brightness, resolution. aspect ratio, frame rate (scan), etc. In general, everything that was required!

Program AIDA 64 works in the same way: you need to open the same tab "Display/Monitor" : you will see approximately the same information (by the way, the information displayed also depends on the model of your monitor; the screen below shows the properties of the Dell Inspiron 3542 - LG Philips LP156WHB (Dell DCR74) laptop monitor).

The program can show slightly more extensive information ASTRA 32. It has a whole section dedicated to monitors connected to your computer (laptop). By logging into it, you will find out almost all the data about your monitor that can be obtained (probably as much as is in the passport for this product).
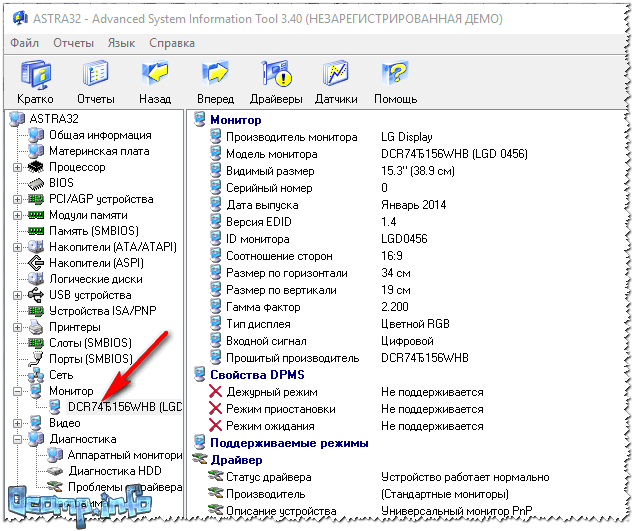
ASTRA 32 - monitor: manufacturer, release date, gamma factor, aspect ratio, serial number, monitor ID, display type, input signal, firmware manufacturer, driver status, etc.
Method number 3: in properties (via the Windows Control Panel)
You can also get partial information about the monitor in Windows. To do this, you need to open the control panel at the following address:

Next among the devices, you should see your monitor. You need to right-click on it and go into it properties or options. This way you will know current resolution (and as much as possible) sweep frequency, monitor model (some information may not be available if you do not have drivers installed for your monitor (not to be confused with video card drivers!)).
That's all I have for this sim, special thanks in advance for any additions. Good luck identifying the type and model!







