How to delete unnecessary Windows restore points. Deleting system restore points
Unnecessary system restore points, that is, irrelevant backup copies of Windows user settings, take up system partition space to no avail. In addition to this, they can cause characteristic difficulties for novice users when choosing a reserve.
This guide will tell you how to delete restore points using standard OS tools and special utilities.
How to leave only the last point
1. Press the “Win” and “E” keys simultaneously.
2. Right-click on the C drive icon.
3. In the context menu, select “Properties”.
4. On the properties panel, click Disk Cleanup.

5. In the new window, click “Clean up system files”.

6. Upon completion of the operation, the “Advanced” tab will appear in the same window. Left click on it.
7. In the “System Restore…” section, click “Clean up…”.

8. In the additional request that appears, confirm the execution of the command: select “Delete”.

Delete all points
1. Press the key combination “Win” + “Pause/Break”.

2. On the left side of the “System” window, click “Protection...”.
3. In the “System Properties” settings panel, on the “Protection...” tab, in the “Options” block, click “Configure...”.

4. To delete all restore points, click “Delete”.

5. In the window that opens with a warning that after cleaning you will no longer be able to use old copies of the settings, click “Continue”.

6. After deleting the points, a message indicating the successful completion of the operation will appear on the display, click “OK” in it.
Selective deletion
To selectively remove unnecessary backups, use one of the utilities described below.
QRM Plus Manager
A tool for managing restore points. It has a user-friendly interface and uses a minimum of PC resources. Installs quickly.
1. Download the utility from a trusted resource. Install into the system.
2. Right-click on a space free from shortcuts on the desktop.
3. In the menu that opens, place the cursor on “QRM Plus”. And then in the additional panel, click “... Manager”.

4. In the manager panel, click the mouse to select the point that you want to remove.

5. Click the "Delete" button.
Advice! Using the QRM Plus utility, you can also create points (Create) and restore OS settings from them (Restore).
A powerful program for cleaning, repairing and tuning the Windows operating system. Endowed with a user-friendly interface. It has a solid set of useful functions for directory and registry prevention.
1. Download the free version of the program from the manufacturer’s website - piriform.com/ccleaner. Install on PC and launch.
2. In the CCleaner window, go to the “Tools” tab.
3. Click the “System Restore” section.

4. In the adjacent block, click on the point you want to get rid of.
5. Click "Delete".
How to restore from a given point?
1. Press the “Win” + “Break” keys together.
2. Open the “System Protection” section.
3. In the “System Restore” block, click the “Restore…” button.
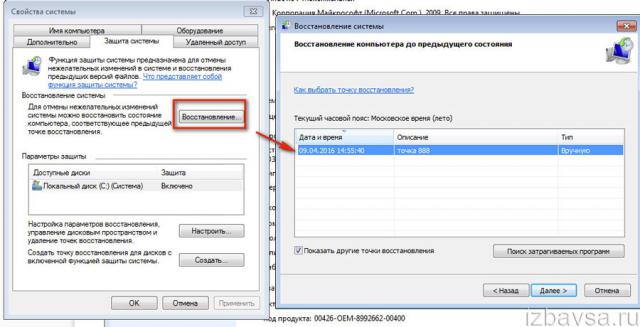
4. In the list that opens, click on a point. Click Next.
5. In the “Confirmation...” window, click “Done”.
6. Wait for the operation to complete.
Successful Windows cleaning!
Restore points disappear Windows 7, I can’t do anything, after rebooting the computer there is nothing, why do you think this happens? I use a laptop. Victor
Restore points disappear
This problem occurs for many reasons, let's look at most of them. The information in our article is, to one degree or another, suitable for both operating systems Windows 7 and Windows XP. Sometimes the user accidentally turns off System Protection for a Local Disk, of course all restore points disappear and are not created again. From the very beginning, check whether System Protection is enabled for that Local disk where points are NOT created or lost. Start->Control Panel->System and Security->System->System Protection. You can also read the article.
Tune

- By default, Windows 7 has System Protection enabled for the drive (C:). It is important that at least 15% of disk space is allocated for recovery points.
- Many times in my practice it happened that the user installed a non-original build of Windows and it already had System Restore disabled by default for all disks.
- It often happens that two operating systems are installed on a computer, the older Windows XP and the younger Windows 7. When creating a restore point in Windows 7, you should know that it will exist until the first launch of Windows XP. When you later boot into Windows 7, all restore points will be lost, just like previous versions of files. To solve this problem, read our article:.
- Also restore points disappear due to the fault of utilities that clean your computer from various debris. For example, the FreeSpacer program or the CCleaner registry cleaning utility can easily delete restore points. Such programs must be configured manually. You must include the System Volume Information folder, which is responsible for storing recovery points, as an exception in the settings of such programs.
- You cannot create a restore point on disks with file systems. These file systems do not support the creation of shadow copies, which contain information about changes to system and user files. Windows 7 uses shadow copies to create restore points.
- Look in Computer management->Services, is the Windows Backup service enabled, as well as the service Shadow copy, responsible for creating restore points.
- If you use a laptop or netbook, restore points will not be created when the charger is disconnected. If the battery is powerful enough, you can disable this option in Task Scheduler. Start->Run->taskschd.msc.
Open the Task Scheduler Library\Microsoft\Windows\SystemRestore branch on the left, then go to the properties of the SR item.

The Triggers tab is responsible for scheduling the creation of recovery points; you can customize it for yourself.
In the Conditions tab, cancel the option Run only on mains power and your laptop will create restore points regardless of whether it is connected to power or not. Uncheck the box there Run a task when the computer is idle and the laptop will create a restore point without waiting 10 minutes by default.
Just in case, make sure there is a checkmark in the Parameters tab Run a task immediately if a scheduled run is missed..
Restore points are one of the key ways to return Windows to a working state if any problems arise. However, you should understand that they can take up quite a lot of space on your hard drive if they are not removed in a timely manner. Next, we will look at 2 options for how to get rid of all irrelevant restore points in Windows 7.
There are quite a few methods for solving this problem, but they can be divided into two categories: using third-party programs or operating system tools. The first usually provide the opportunity to independently select those backups that need to be deleted, leaving the necessary ones. Windows limits the user's choice by deleting everything at once. Based on your needs, select the appropriate option and apply it.
Method 1: Using programs
As mentioned earlier, the functionality of many utilities for cleaning Windows from garbage allows you to manage restore points. Since the majority of computers have CCleaner installed, we will look at the procedure using this example, and if you are the owner of similar software, look for the appropriate option among all the available functions and remove it in the same way as the recommendations described below.

Method 2: Windows Tools
The operating system, of course, itself knows how to clean the folder where recovery points are stored, and does this at the user’s request. This method has one advantage and disadvantage over the previous one: you can delete all points, including the last one (CCleaner, we remind you, blocks cleaning from the last backup), but selective deletion is not possible.

By the way, in the parameters window "System protection" You can not only view the volume that backups currently occupy, but also the ability to edit the maximum size allocated for storing recovery points. Maybe there is a fairly large percentage there, which is why the hard drive is full of backups.
So, we looked at two options for getting rid of unnecessary backups, partially or completely. As you can see, they are not anything complicated. Be careful when clearing your PC of restore points - they can come in handy at any time and fix problems that arise as a result of software conflicts or rash user actions.
Greetings to all readers of the Public PC blog. In this article, you will learn in detail how to delete restore points in Windows 7. Using a restore point, you can go back in time and the state of your computer will also return. Before we learn how to delete all system restore points in Windows 7, let's remember why this is needed and what it is all about.
So, using the “Recovery Checkpoint” you can rewind time and... However, each such return point clogs the hard drive memory. You can delete such restore points and thereby free up computer memory.
How to delete restore points in windows 7? Easily!
If you want to know how to delete restore points in Windows 7, then you need to do the following:
Method 1: Deleting restore points (except the last one).
Thus, you have started preparing the system for disk cleanup.
- In the new “Disk Cleanup (C)” window, do the following:
- Advanced Tab –
- “System Restore and Shadow Copies” –
- "Clear."
When the system asks about deleting restore points, click “Delete”.
Here’s another way to delete absolutely all (including the last one) system restore points in Windows 7.
Method 2: Delete all restore points.
- “Start” – “Control Panel”.
- Set View: Small Icons.
- Click on "System".
4) In the window that appears on the left side, select “System Protection”.
5) Tab “System Protection” – “Configure”.
In the window that appears, we check the correctness of our actions. The following should be written: "Removing all restore points, including system settings and previous versions of files".
6) Click “Delete”.
Now you know how to remove . I hope the information was useful to you and you will leave your feedback in the comments, and also subscribe to blog updates at the end of the article. I will be very grateful to you for this. I wish everyone peace and health in your families.
With UV. Evgeny Kryzhanovsky
Windows provides several ways to protect itself. That is, the operating system by default contains mechanisms that allow you to quickly restore the computer to its functionality after a failure.
One such mechanism is Windows restore points.
What is a Windows Restore Point
Restore point is a set of parameters and important system files that determine the state of the operating system at a particular point in time. That is, when creating a restore point, Windows “preserves” the most important things responsible for its performance. All conserved information is stored in a protected area of the hard drive. In the event of a failure or failure of the operating system, you can use a restore point and restore the operating system to the state in which it was at the time the restore point was created.
At the same time, it is IMPORTANT to understand that we are talking ONLY about the state of the operating system, that is, about the state of its most significant files, and not about user files or an image of the entire system disk.
For example, a virus can damage system files, causing the computer to stop booting or causing a blue screen of death to appear. This can also be caused by incorrect driver installation, operating system updates, or even the installation of some program.

In such a situation, a restore point will allow you to very quickly solve the problem by returning the system files to the state they were in before they were damaged or changed.
Restore points allow you to undo recent changes to the operating system, but their use will only be truly effective if they are created in a timely manner. This means that restore points should be created regularly, and also before each potentially unsafe action, such as installing a driver or new application on the computer.
Usually the Windows operating system itself copes with this task, but here it is worth understanding that you will have to pay for such insurance and in this case it is not about money, but about hard drive space. Restore points can take up a significant amount of space, especially if they are created regularly.
Many users do not know about the existence of restore points, but have encountered . Quite often there is a direct connection here and deleting old restore points can free up additional gigabytes, and sometimes tens of gigabytes, on the system disk.
I also want to note that restore points are not always useful and I personally disabled their creation in Windows. But this does not mean that they are completely useless. Each user has his own algorithm for restoring the functionality of the operating system, and this algorithm depends on how the person uses the computer, that is, on how his work on the computer is organized. For example, I have had a virtually unchanged set of programs on my computer for a long time, and my personal files have always been located on a non-system drive. For this reason, in the event of a failure, it was easier for me to use a pre-created image of the system disk and restore the system partition with all the applications I needed in half an hour, rather than without a guarantee to conjure with recovery points. But still, sometimes their use is completely justified.
If you experiment with programs, periodically install something new, or are going to change something in , then restore points will help you avoid possible problems.
So let's look at the recovery settings.
Configure system recovery options
Recovery settings can be found in the window Properties of the system. You can access this window in different ways, for example through Windows 10 search.

Or by calling the context menu on the element This computer in Explorer, select Properties.

In the window that opens, go to .

The creation of restore points can be enabled for all disks, but it is logical to use this tool only for the system partition. In area Security settings we see for which disks protection is enabled or disabled.

If you want to use recovery points for the system disk, but its protection is disabled, then select the disk and click on the button Tune. Then we turn on system protection and can immediately determine the amount of disk space that we are willing to sacrifice to create restore points.

And here again a compromise is needed. The fact is that the more disk space you allocate for recovery points, the more of them will be saved. As soon as the allotted space is filled, the oldest points will be gradually deleted, replaced by newly created ones.
If you allocate too small a volume, this may lead to the fact that recovery points simply will not be created even when disk protection is turned on.
Also, quite often users have a completely logical desire to transfer recovery points to another disk or even removable storage media, for example, a flash drive. Unfortunately, this cannot be done, since recovery points must be stored on the disk that is being protected.
How to create a Windows restore point
So, if protection is enabled, restore points are created automatically when you install new applications, drivers or Windows updates, but sometimes you need to create them manually. For example, you are going to make some changes to the Windows registry. In this case, it’s worth being on the safe side and creating a recovery point in case of unforeseen complications.
To create a Windows restore point, click on the button Create(in the window Properties of the system, tab). Next, you can specify a custom name for the recovery point. The date and time will be added automatically.
 
It will take some time to create the restore point, after which you will see success messages.
Where are Windows restore points located?
As I already mentioned, recovery points are stored in a certain area of the protected disk - this is the folder .

It is hidden and located in the root of the protected disk. You can see it by turning on the display mode for hidden folders and files in Conductor. But entering the folder and deleting something in it will not work, since it is protected by the system.

For the same reason, programs do not have access to this folder. Therefore, if you are using the program Conductor If you try to estimate the amount of free disk space, this folder will not appear in the displayed volume, which makes many users puzzled by the question of the loss of free space on the system disk.
But there is no need to work directly with the folder. I mention it only because some novice users have questions about its purpose.
How to roll back Windows to a restore point
So, if Windows suddenly starts acting up, then one of the options to solve the problem is to roll back its state to the last successful restore point.
There are several ways to do this and the easiest is through the section System Restore.

Click on the button Restore and the recovery wizard starts. Here we are immediately informed that the recovery does not affect the user's personal files, however, applications, drivers and updates installed after creating a restore point may be deleted.


If the system created restore points automatically, the wizard can recommend one of the latest points. You can also select a restore point manually by specifying it in the list.

After selecting a point, click on the button Ready and Windows will be restored to the specified state. After the computer restarts, a message indicating the successful completion of this operation will appear.
How to delete restore points
If you do not use and do not plan to use recovery points, but find that protection is enabled for one of the disks, then in the disk protection settings you can delete the already created recovery points and then disable the protection.

Also, many optimization programs allow you to delete system restore points, and some of them clear them by default. Therefore, if you use some cleaners and clear everything that the utility offers by default, then most likely delete all restore points.
I have said it many times and will repeat it again: any program is just a tool and cannot be relied on unconditionally. This is why I do not recommend that novice users clean their computer using such utilities, since in inept hands these programs do more harm than good.
But in any case, it’s worth knowing that all “cleaners” can delete restore points. For example, the program copes with this perfectly - in the section Service subsection System Restore You can select and delete unnecessary restore points.

Recovering a deleted restore point
A fairly common question is how to restore a restore point if it was deleted accidentally or mistakenly.
Unfortunately, NO way.
Once I was present while trying to restore erroneously deleted restore points. To do this, the computer's hard drive was connected to another computer, on which, using a program to recover deleted files, the person tried to restore the deleted restore point. But this did not lead to anything, only a lot of time was wasted.
I see no point in such dubious transactions. If the restore point has already been deleted, then it is much easier and faster to reinstall Windows if problems arise. Well, it’s even better to have an image of the system with all the necessary programs. And I will talk about creating such images in the next post.
Don't miss the opportunity to do a good deed:







